Hello cyber learners,
In today's digital age, cybersecurity is a top priority for any organization that values the security of its sensitive data and network infrastructure. One of the most critical components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is the deployment of an Intrusion Detection System (IDS). An IDS is a software application that monitors network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
In this blog, we will cover everything you need to know about IDS, including their functioning, advantages, disadvantages, different types, and how to choose the right system for your organization. Additionally, we will explore the benefits of using IDS and IPS and how they can prevent common attacks like CSRF and XSS. So, Let's get started!
- What is Intrusion Detection System
- What is Intrusion Prevention System
- How Intrusion Detection System Works
- How Intrusion Prevention System Works
- Differences between IDS and IPS
- Types of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
- The benefits of using intrusion detection and prevention systems
- How do intrusion prevention systems (e.g. Snort) prevent CSRF and XSS attacks?
- How to choose the right IDPS for your organization?
- The Future of intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Conclusion
What is Intrusion Detection System
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security system that monitors network traffic or system activity for any suspicious or unauthorized behavior. The system examines the data packets that are transmitted over the network and looks for signs of malicious activity. If any suspicious activity is detected, the IDS will generate an alert or notification, which can be used to initiate an appropriate response.
What is Intrusion Prevention System
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are similar to IDS, but they are more proactive in their approach. IPS systems not only detect but also block malicious traffic to prevent an attack before it happens. IPS is integrated with the firewall and can automatically block traffic that violates network security policies.
IPS can operate in different modes, such as inline mode and promiscuous mode. In inline mode, IPS blocks the traffic that it identifies as malicious. In promiscuous mode, IPS will alert the network administrator, but it will not block the traffic.
IPS is an advanced form of IDS that not only detects suspicious activity but also takes immediate action to prevent the attack. An IPS can block the source of the malicious traffic, re-route the traffic, or terminate the connection. IPS can also work in tandem with other security systems such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and vulnerability scanners.
How Intrusion Detection System Works
IDS works by analyzing network traffic and comparing it to known signatures of malicious activity. The system is programmed to identify specific patterns in the traffic that could indicate malicious activity. IDS can also use behavioral analysis to identify suspicious activity that may not be captured by signature-based analysis.
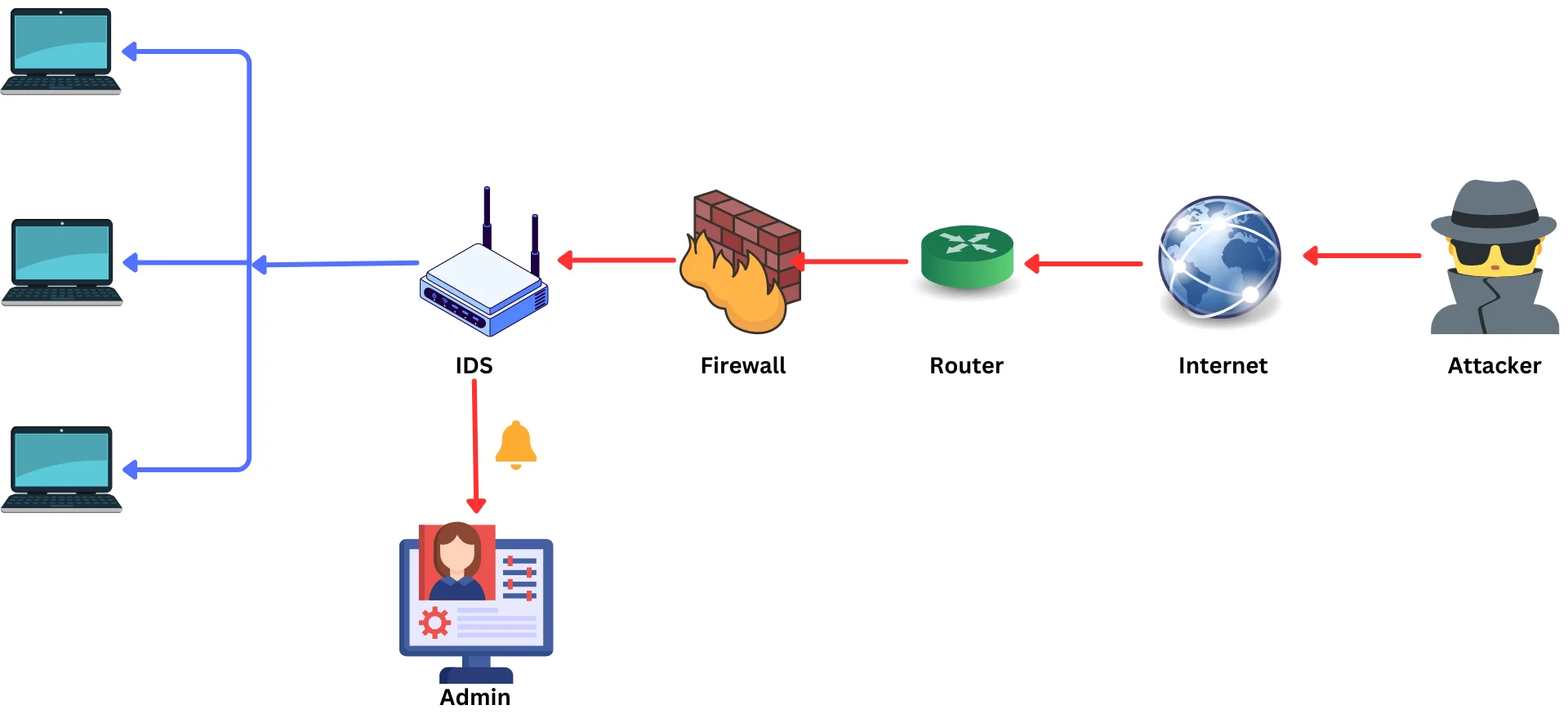
Once the IDS has identified suspicious activity, it generates an alert that is sent to the network administrator. The administrator can then take appropriate action to respond to the alert, such as blocking traffic from the source of the malicious activity or shutting down the connection.
How Intrusion Prevention System Works
IPS works in a similar way to IDS, but it has the added capability of stopping malicious activity before it can cause any harm. IPS uses signature-based analysis, behavioral analysis, or a combination of both to identify malicious activity. Once the IPS has identified malicious activity, it takes immediate action to block or prevent the attack.
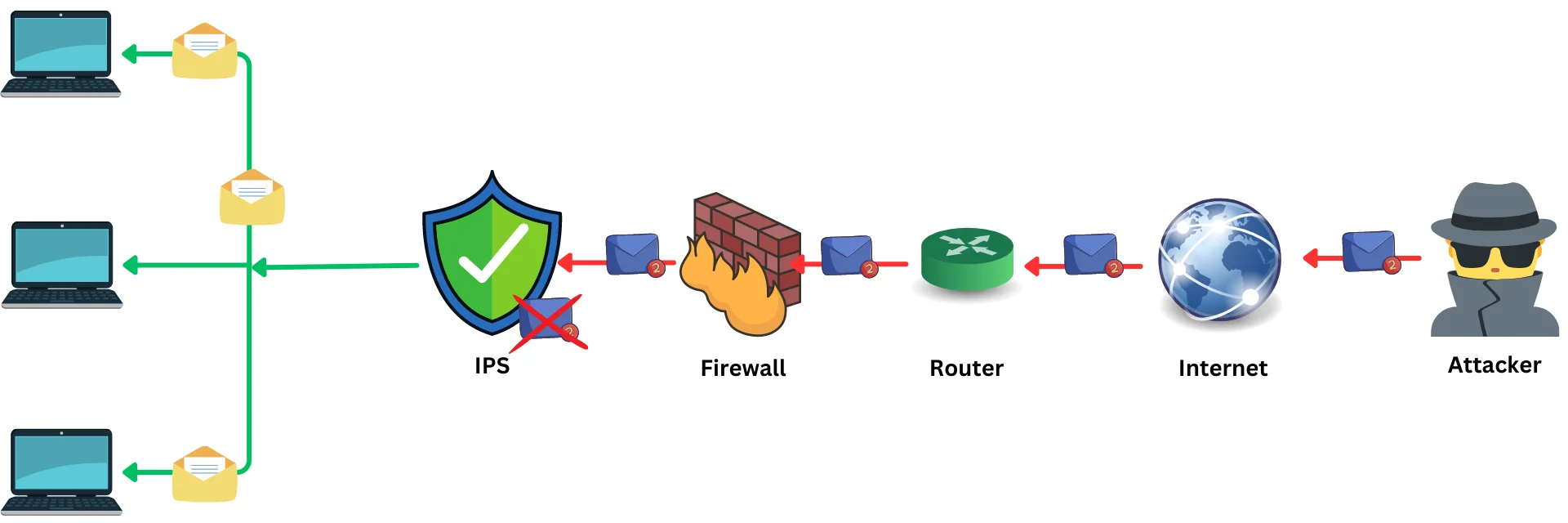
IPS can be deployed in-line or out-of-band. In-line deployment involves placing the IPS directly in the path of network traffic, while out-of-band deployment involves placing the IPS on a separate network segment. In-line deployment offers better protection but can potentially affect network performance.
Differences between IDS and IPS
IDS (Intrusion Detection System):
- A passive security system that monitors network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
- Identifies suspicious patterns in network traffic and generates alerts for the system administrator to investigate.
- Generates alerts for system administrators to investigate suspicious activity.
- Logs traffic patterns and suspicious events for future analysis.
- Can help with incident response and forensic investigations.
IPS (Intrusion Prevention System):
- An active security system not only detects suspicious network activity but also takes action to prevent it.
- Blocks traffic that is identified as malicious or anomalous.
- Modifies network traffic to remove or neutralize threats.
- Takes action to prevent or neutralize threats.
- Can prevent attacks from occurring in the first place.
The main difference between an IDS and an IPS is that an IDS alerts the administrator of suspicious activity, while an IPS will actually take action to block or stop suspicious activity. Both technologies are important for a comprehensive security program and should be used in conjunction with other security measures.
What is IDPS?
Ans. IDPS, or Intrusion Detection and Prevention System, is a security technology that combines both intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). It monitors network traffic and system activities for unauthorized access, malicious activities, and policy violations. The integration of IDS and IPS allows IDPS to not only detect but also prevent malicious activities from occurring in real-time. This makes IDPS an essential security technology for organizations to safeguard their networks and systems against a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
Types of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
There are many types of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) available today. Some are designed to work with specific types of networks, while others can be configured to work with any type of network. The most common types of IDPS include:
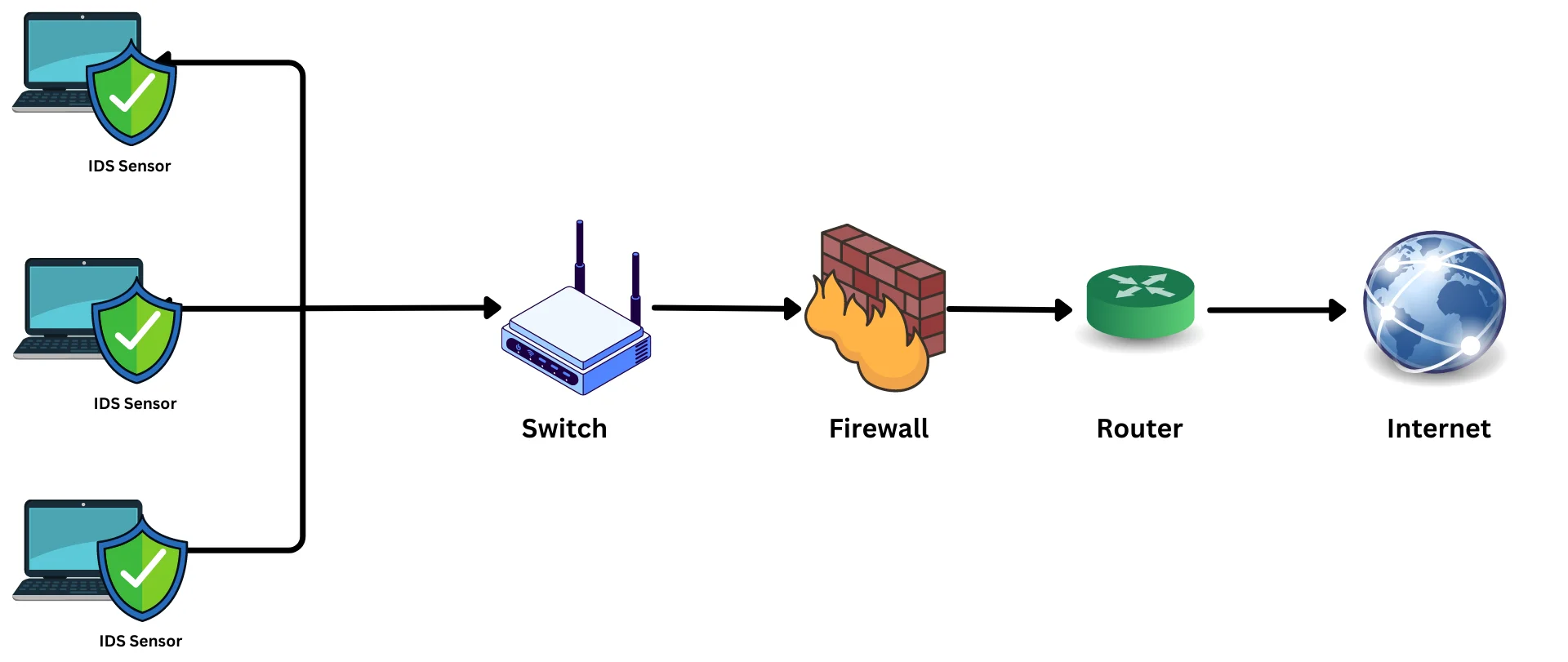
- Network-based IDPS: A network-based IDPS resides on a network perimeter device, such as a firewall or router. It monitors all traffic that enters or leaves the network and can take action to block malicious traffic.
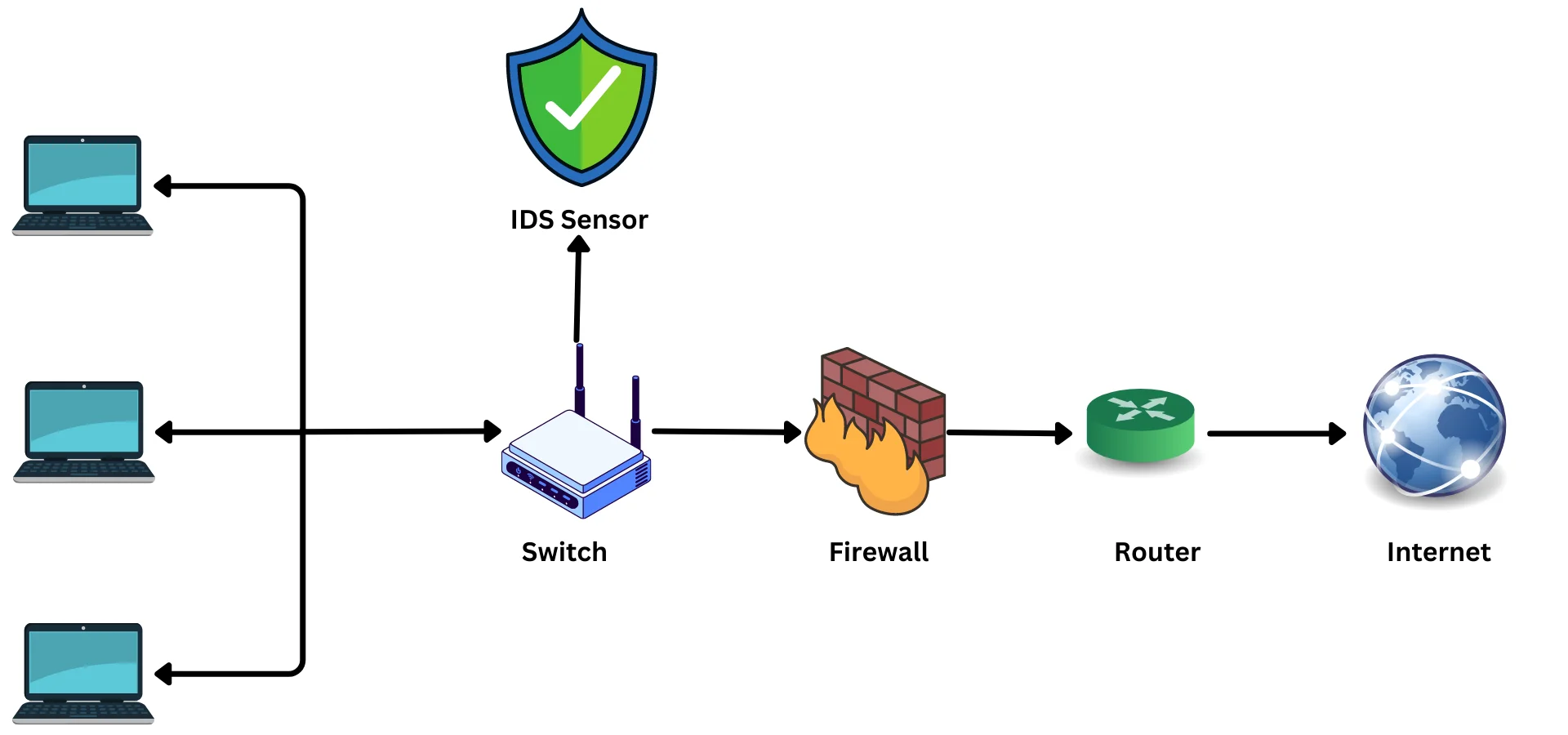
- Host-based IDPS: A host-based IDPS resides on a server or workstation. It monitors all traffic to and from the host and can take action to block malicious traffic.
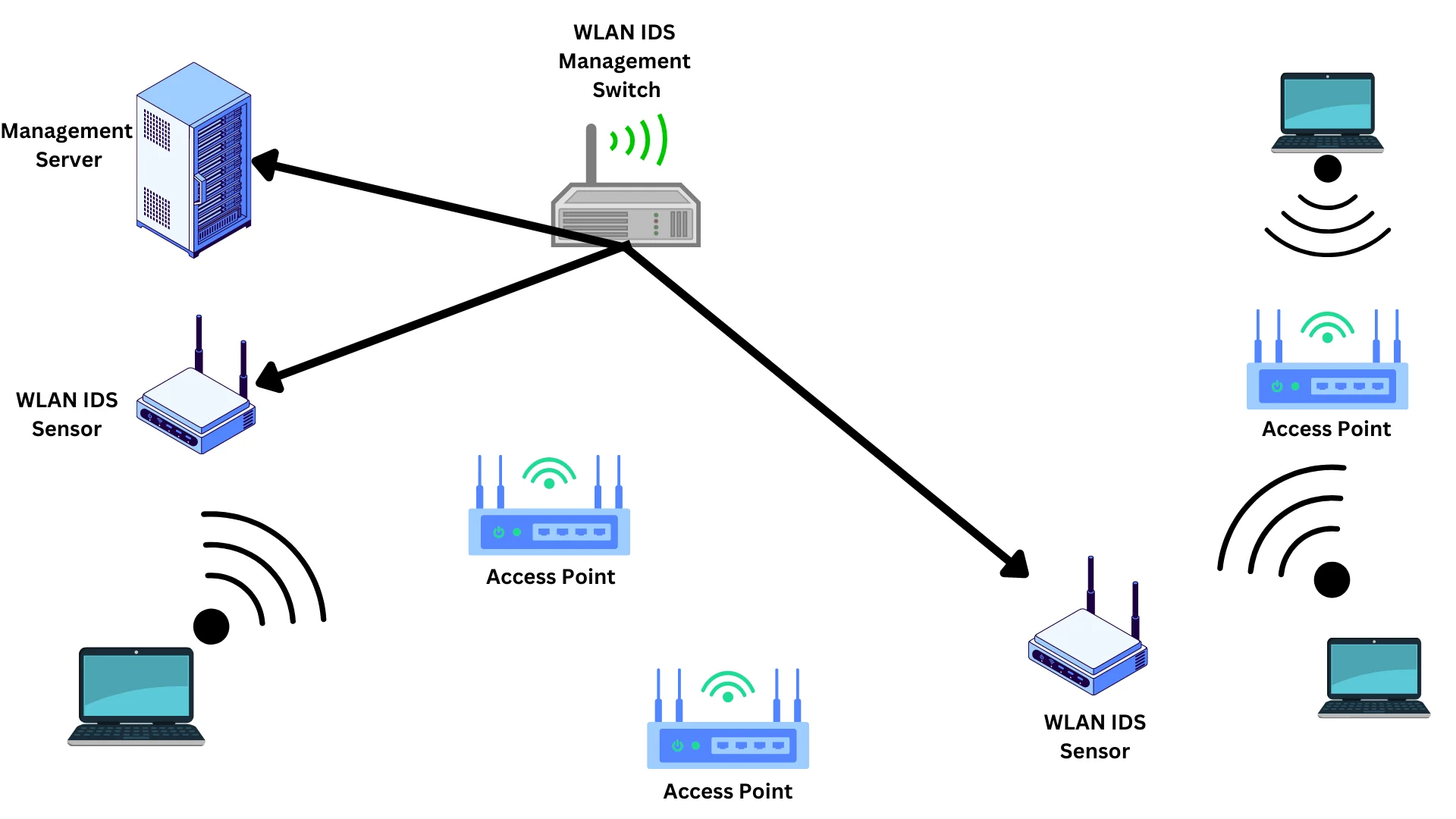
- Wireless IDPS: A wireless IDPS is designed to monitor and protect wireless networks. It typically resides on a wireless access point or controller. A wireless IDPS works by analyzing wireless network traffic in real-time, looking for patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
The benefits of using intrusion detection and prevention systems
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) offer many benefits for organizations looking to improve their security posture.
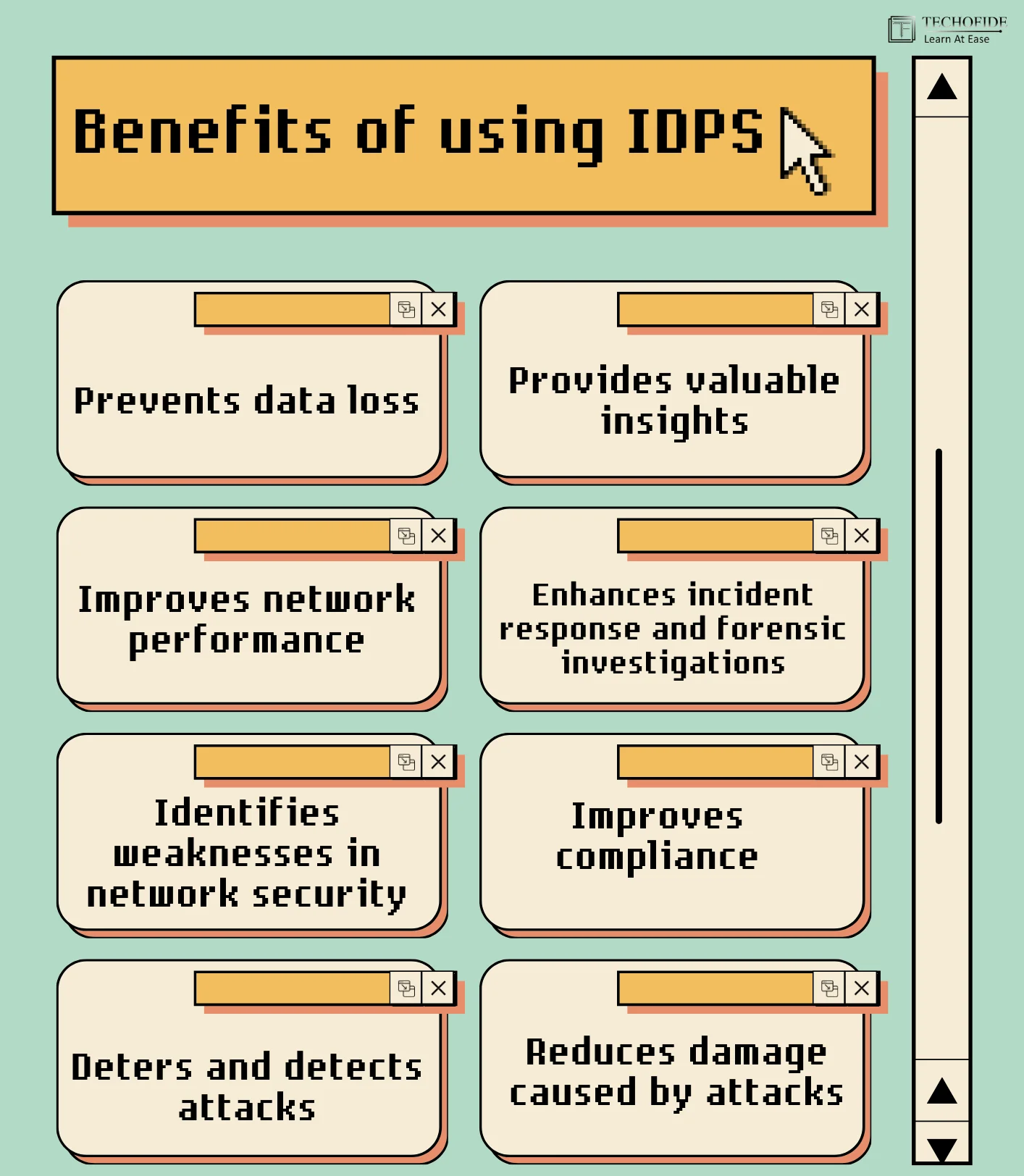
- Prevents data loss: IDPS can detect and block attempts to access, modify, or delete sensitive data, protecting against data breaches and data corruption.
- Improves network performance: IDPS can reduce network traffic and improve speed and reliability, helping to optimize network performance.
- Identifies weaknesses in network security: IDPS can reveal potential vulnerabilities in the network, enabling organizations to take proactive steps to improve security.
- Deters and detects attacks: IDPS can monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, helping to identify and block attacks in real time.
- Reduces damage caused by attacks: IDPS can prevent or mitigate the impact of attacks, minimizing the potential damage to the network and organization.
- Provides valuable insights: IDPS can analyze attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), helping organizations to better understand the nature of cyber threats and improve their security defences.
- Enhances incident response and forensic investigations: IDPS can provide critical information and evidence to support post-incident analysis and forensic investigations.
- Improves compliance: IDPS can help organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements by providing enhanced security monitoring and reporting capabilities.
Overall, IDPS can significantly enhance an organization's security posture by detecting and preventing attacks, improving network performance, and providing valuable insights into cybersecurity threats.
How do intrusion prevention systems (e.g. Snort) prevent CSRF and XSS attacks?
In order to prevent CSRF and XSS attacks, intrusion prevention systems (IPS) use a combination of signature, heuristic, and behavioral-based detection methods.
Signature-based detection looks for known patterns of attack in web traffic. Heuristic-based detection uses a set of rules to identify suspicious traffic. Behavioral-based detection monitors the behavior of users and flagging anomalous behavior that could indicate an attack.
In order to prevent CSRF attacks, IPS systems typically look for requests that contain unexpected or suspicious parameters. For example, a request that contains a session ID but no other parameters might be flagged as suspicious.
In order to prevent XSS attacks, IPS systems typically look for requests that contain suspicious code. For example, a request that contains HTML code in a parameter that is not normally expected to contain HTML code might be flagged as suspicious.
One popular tool used for intrusion prevention is Snort, which is an open-source network intrusion prevention and detection system. Snort uses signature-based detection and can also employ heuristic-based and behavioral-based detection methods.
Snort is a useful tool for finding and preventing XSS attacks. It can be configured to monitor HTTP traffic for suspicious requests that contain potential XSS payloads, such as script tags or encoded JavaScript. When Snort detects such payloads, it can take action to prevent the attack, such as blocking the request or alerting security personnel.
How to choose the right IDPS for your organization?
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) are an important part of a comprehensive security strategy, but choosing the right one for your organization can be a challenge. There are a number of factors to consider, including your organization's size, budget, and security needs. IDPS should be able to detect a wide range of attacks, including those that exploit vulnerabilities, use malware, or generate malicious traffic. It should also be able to prevent attacks by blocking malicious traffic or taking other corrective actions. An IDPS should be compatible with the network devices, operating systems, and applications in your environment.
let's look at some key features to notice when choosing IDPS for your organization.

When choosing an IDPS for your organization, consider the following factors:
Size: The size of your organization plays a critical role in choosing the right IDPS. The IDPS must be able to handle the traffic volume and the number of devices in your environment. Choosing an IDPS that is too small could leave you vulnerable, while selecting one that is too large might be unnecessary and cost-prohibitive.
Budget: The cost of an IDPS is another crucial factor. It is essential to choose an IDPS that fits within your budget. Some IDPS solutions are more expensive than others, and choosing a solution that is too expensive can drain your organization's finances. However, opting for a cheaper IDPS might result in inadequate security coverage.
Security Needs: Understanding the security needs of your organization is key to selecting the right IDPS. The IDPS you choose must be able to detect and prevent the types of attacks that are most likely to target your organization. Consider your organization's industry, size, and potential risks when selecting an IDPS.
Compatibility: The IDPS you choose must be compatible with the network devices, operating systems, and applications in your environment. Before choosing an IDPS, you must ensure that it integrates seamlessly with your organization's existing infrastructure.
Performance: High performance is a crucial factor when selecting an IDPS. The IDPS must have low false positive rates. It should also be able to process high volumes of traffic without adversely affecting network performance. A high-performance IDPS ensures that all traffic is processed promptly, and attacks are detected in real-time.
Management and Reporting: The IDPS you choose should include tools that simplify deployment, configuration, and management. It should also provide comprehensive reporting features that help identify and respond to threats promptly. Good management tools allow the security team to respond to threats quickly and efficiently. Comprehensive reporting features enable the team to identify trends and patterns and make informed decisions.
The Future of intrusion detection and prevention systems
The future of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) looks promising. Technology is constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated. IDPS systems are becoming more effective at detecting and preventing attacks. They are also becoming more user-friendly and easier to deploy.
There are a number of trends that are driving the future of IDPS. First, the adoption of IDPS is increasing. This is due to the recognition of the need for better security and the realization that traditional security measures are not adequate. Second, IDPS vendors are constantly innovating and improving their products. They are adding new features and making their products more user-friendly. Third, the price of IDPS is decreasing. This is due to the increasing competition in the market and the economies of scale.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an Intrusion Detection and Prevention System is an essential tool for any organization looking to secure its network infrastructure and sensitive data. By monitoring network traffic and preventing malicious attacks, IDPSs provide an added layer of security against cyber threats.
In this blog, we have covered the functioning, advantages, disadvantages, different types, and how to choose the right IDPS for your organization. We have also explored the benefits of using IDPSs and how they can prevent common attacks like CSRF and XSS.
In the next part of this series, we will provide a practical demo of the popular IDPS software, Snort. This will include the installation and configuration of rules on both Linux and Windows operating systems. So stay tuned for part 2, and don't miss out on the opportunity to enhance your organization's cybersecurity!
Commonly Asked Questions
Q1. Why are Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) needed?
Ans. IDSs are essential components of modern cybersecurity systems because they provide early detection and prevention of various types of cyber attacks. They help to protect an organization's IT systems from threats, comply with regulations, protect sensitive information, and provide continuous monitoring of network traffic. IDSs can significantly reduce the damage and cost associated with an attack and prevent further spread of the attack. Therefore, organizations of all sizes should consider implementing IDSs as part of their cybersecurity strategy.
Q2. What datasets can I use to test both anomaly-based and signature-based Intrusion Detection Systems?
Ans: There are several publicly available datasets that you can use to test both anomaly-based and signature-based IDSs. These datasets include the KDD Cup 1999, NSL-KDD, UNSW-NB15, DARPA 1998, and CICIDS2017. These datasets contain a diverse range of attack and normal traffic to evaluate the effectiveness of IDSs. Using multiple datasets can ensure a more comprehensive evaluation. Testing IDSs with these datasets can help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems and enhance their overall cybersecurity strategy.
Q3. What makes a good IDS?
Ans. A good IDS should be able to detect and prevent various types of cyber attacks, provide early detection, protect sensitive information, and offer continuous monitoring of network traffic.
Related Blogs
- Snort - Intrusion Detection System & Prevention System | Installation & Use in Windows
- Snort - Intrusion Detection System & Prevention System | Installation & Use in Linux
- What is Website Hacking | Web Application Penetration Testing | Lab Setup
- What is OSINT? | OSINT Framework | Tools for OSINT | Best OSINT Techniques
- What is Smurf Attack? | What is the Denial of Service Attack? | Practical DDoS Attack Step-By-Step Guide
- What is Packet Sniffing? | How to Perform Packet Sniffing | Practical Demo on Wireshark
- What is Metasploit Framework | What is Penetration Testing | How to use Metasploit
- Intrusion Detection System and Firewall