In this blog, we will get the complete basic knowledge about 3d printing and will get to know how does a 3D Printer work, 3D Printing technologies have applications in the various engineering fields and it has a great industrial future. In this blog, will get to know what are the different steps involved in the additive manufacturing process, how a model is designed, and how it is processed further so that we are able to print a 3D product of the desired shape and size.3D printing is often referred as additive manufacturing or rapid prototyping.
3D printing is in fact a very revolutionary idea in the field of digital manufacturing which leads to the making of a product of desired quality and dimension. Especially in the manufacturing industry is has great applications, as the complex shaped product can be manufactured easily using 3D printing methods. Its demand is increasing day by day as digitalization of manufacturing processes reduces the defects in products made, that were observed in ample amounts in traditional manufacturing processes.
What is 3D Printing?
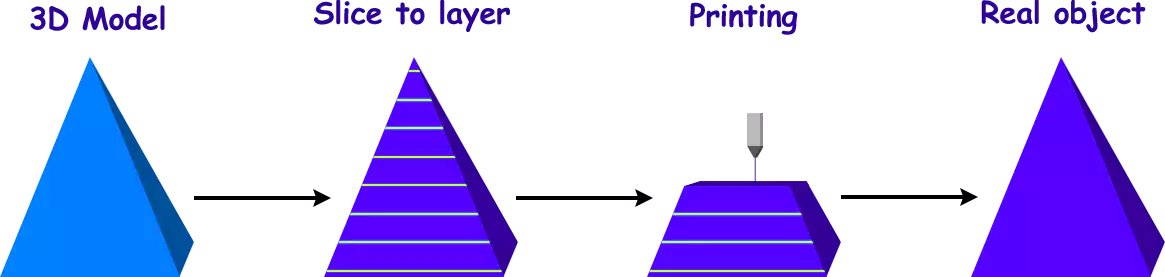
As the name itself suggests, additive manufacturing or 3D printing is simply printing or simply producing a 3D Model.
If we define it in a more formal way, “ Additive manufacturing refers to the process by which digital 3D design data is used to build up a component (basically a 3D Model) by layer by layer depositing material.”
3D Printing is a process in which we make or develop a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model (Digital model implies models made on designing software also known as CAD Models), by laying down various thin layers of material. It converts a digital file (a CAD model ) into its physical form by adding layer by layer of materials. And finally, we get a Physical 3D model.
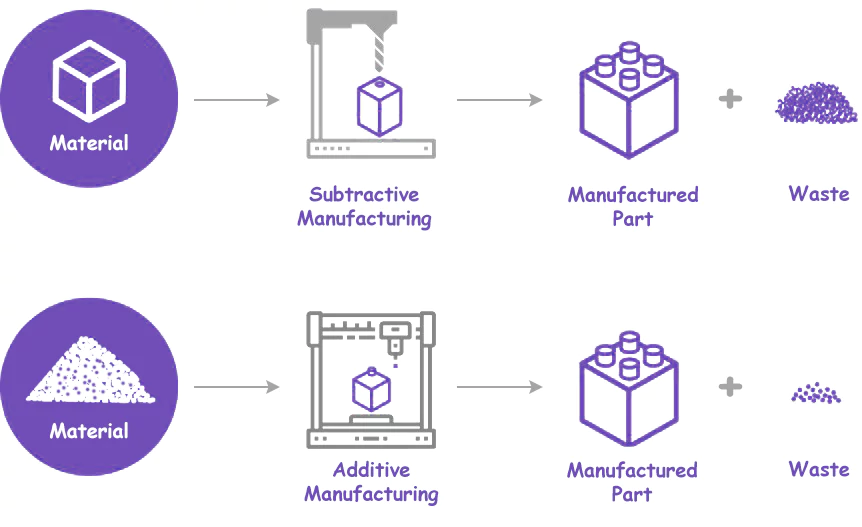
Additive VS Traditional Manufacturing Process
The most basic difference behind 3D printing is that it is an additive manufacturing process, which is based on modern technology that produces a 3D model ( required product), additively, by adding layers with thickness in a few mm. Whereas in traditional processes material removal is the key. Talking about the speeds, the Additive manufacturing process is a time taking process.
Traditional manufacturing, which used to rely on human labor in earlier times, but the world of manufacturing changed with time, and automating these processes such as machining, casting, forming, and molding by using machines, computers, and robot technology.
But still, the basic principle remained the same i.e subtracting material from a larger or bigger block so as to obtain the desired product. Moreover in traditional manufacturing, the making of tools also involves a similar production process. The removal of material leads to wastage of removed material to a large extent which is one major and the most serious problem or limitation in these manufacturing processes. On the other hand, 3D printing creates objects by adding material in a layer-by-layer fashion.
Thus if we observe both of the processes we find that additive manufacturing( 3D printing) to be far better than the traditional processes as it provides more freedom in design and it is material-efficient and energy-efficient at the same time.
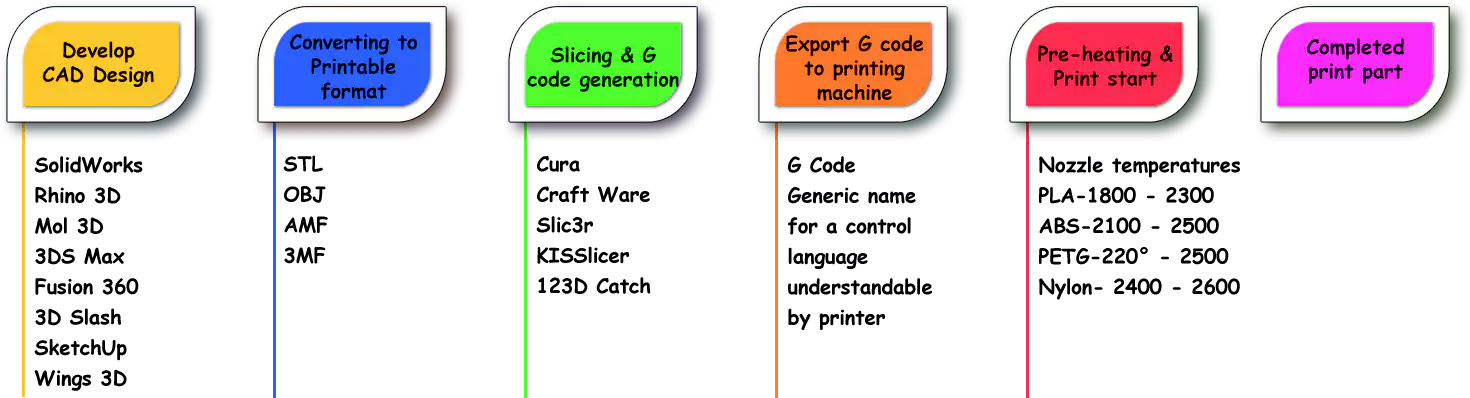
Steps in 3D Printing Process
If we look at the working of a 3D printing process, it includes multiple steps and the whole process can be summarized in 7 basic steps which are as follows:
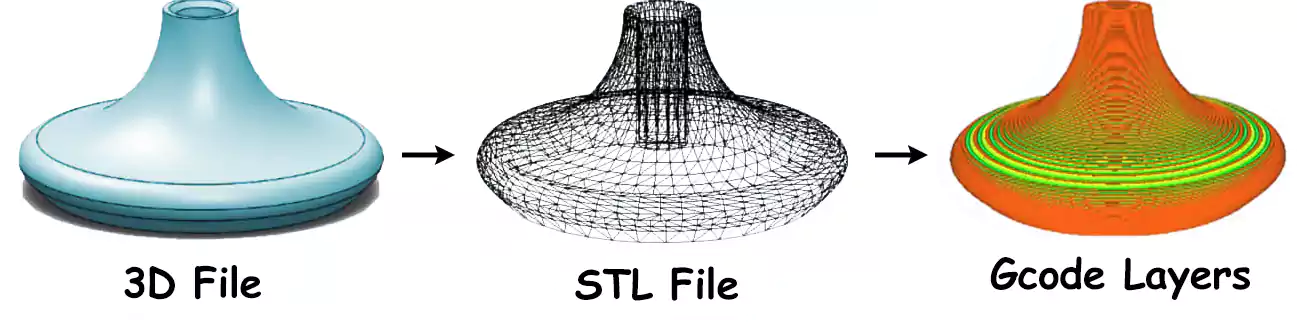
Step 1 – Creating a 3D model
We create a 3D model of our desired product in CAD software like Fusion 360.
Step 2 – Converting into STL file
The CAD model is then converted into an STL file to slice down the 3D model into a combination of thin layers.
Step 3 – Transfer of STL file
The STL file is then saved and transferred to the 3D printer using a suitable custom machine software.
Step 4 – Machine set up
Consumables( material to be used) are loaded into the machine and the 3D printer is set up with the desired printing parameter.
Step 5 – Building of product
The printer starts making the model of the product as per the motion coding done in it using G and M codes.
Step 6 – Removal of part
The part (product) is then removed from the building platform of the printer.
Step 7 – Post-processing process
In this, the building product is cleaned, polished, and painted as per the need.
3D Model Making with CAD Software
This software is used to create a 3D model of the desired product. This software is also commonly known as CAD software. Once the model is made then the further steps are much easier. To design a 3D model we need to learn at least one CAD software. Few of this software that can be used to design a 3D model of the desired product that we are going to produce using 3D printing technology are as follows:
Slicing of the Model using Slicing Softwares
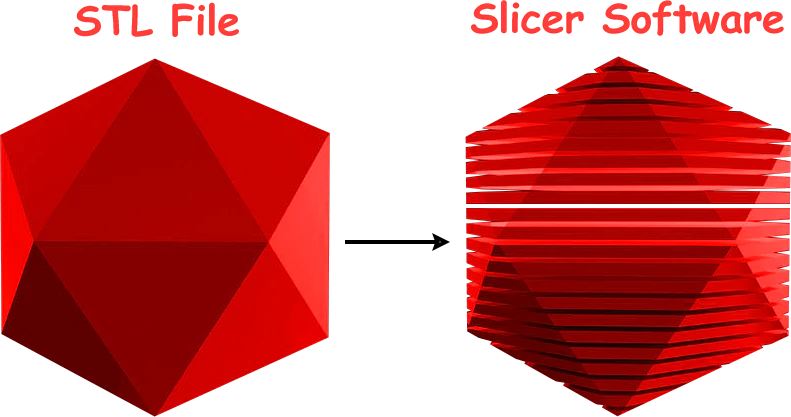
The basic role of this software is to slice down the given model into thin layers. This software takes the CAD model and slices it into very thin layers and then accordingly turns this model into suitable G code.
The slicing software also involves the functions like setting temperature, print speed, the height of the layer, and so on in a 3D printer by altering the G codes.
The 3D printer then reads these final G codes and accordingly starts working and starts building the model by deposition the material in a layer by layer fashion according to the instruction given to it via a set of G codes.
Few of the slicing software are as follows:
How does a 3D Printer work?
Once the modeling process and slicing of the model are done, then comes the time when the role of the 3D printer comes into the picture. Now let's see how does a 3D printer work.
A 3D printer works in a similar way as any normal printer works. In the direct 3D printing process, a nozzle moves in a reciprocating manner while dispensing or ejecting a wax or polymer layer by layer and then waiting for one layer to dry and then further adding the other layer.
It basically adds various 2D layers one over the other, ultimately leading to the final 3D model.
The material used in the 3D printers can be a metal powder( eg. Titanium), Polymers, thermoplastic, powdered ceramics, Biomaterials, etc. Various materials that a 3D printer uses in order to create a product or 3D model are:
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS): Plastic material which is easy to mold and hard to break.
- Carbon Fiber Filaments: Used to create lightweight and strong objects.
- Conductive Filaments: Used to print electric circuits without the need for wires.
- Flexible Filaments: Used to print tough and bendable products.
- Metal Filament: To print metallic objects.
- Wood Filament: Made of wood power plus polymer glue and used to print wooden objects.
- Photopolymers: Photopolymer is a light-sensitive resin that changes its properties when exposed to light especially ultraviolet light.
There is various type of 3D Printing processes, which are as follows :
1.Vat Photopolymerisation :
- Liquid polymer is spread on the building platform.
- The liquid is then turned into a solid by exposing it to UV light.
- First, the 3D model is designed and then the 3D printer uses Digital light processing technology, which projects the UV light on the liquid polymer.
- Then only that portion where UV light is poured, only that area gets solidified
- This entire process of liquid polymer being drained and then being exposed to UV light is repeated till the 3D object is completely made.
2.Material Jetting :
- The printing head is placed above the Build Platform
- Material droplets are then dropped onto the desired space of the build platform with the help of a print head.
- Droplets are then left to solidify.
- Once the first layer is solidified then the further layer is made in a similar fashion.
- Then layer is left to cool down and is hardened or further processed using UV light
- Finally, the 3D model is made.
3.Binder Jetting :
- Powder of the material is spread over the building platform.
- Adhesive binders are deposited on the powder according to the need with help of the print head.
- Lowering of build platform takes place for making the next layer.
- Powder that is not fixed with the help of adhesive is left as it is.
- The process is continued till the 3D model is ready.
- Then the model is finally cleaned and ready for use.
4.Material Extrusion :
- Material is deposited onto the build platform with the help of a nozzle where it is required to be deposited for the first layer.
- Then the next layer is added to the previous layer.
- The layer is then fused together, as the material is deposited in the melted state.
- By these steps, the layer is added, and finally, we get the final 3D model.
5.Powder Bed Fusion :
- Also sometimes referred to as Selective laser sintering.
- Material Layer of the thickness of approximately 0.1mm is deposited onto the build platform.
- Then a laser is used to fuse this material according to the need of the first layer.
- Then for the next layer, a new layer of material is added and spread with the help of a roller.
- Further, the steps are similar to the previous ones.
- These steps are repeated until the final 3D model is completely made.
6.Sheet Lamination :
- The material is kept in the place of the cutting bed.
- Then according to the need of layer, the material is cut from the layer with the help of a laser and knife.
- Then the next layer of material is added.
- The material is attached to the previous layer with the help of adhesive.
- These steps are repeated until the complete formation of the 3D model.
7.Direct Energy Deposition :
- A multi-axis arm with a nozzle moves around an object of fixed shape.
- Material is poured via a nozzle onto the surface of the object.
- Material is provided in the form of wire or powder.
- Material is fused with the help of Laser, Electron beam, etc.
- Then the next layer of material is deposited
- Further steps are similar to previous steps.
- These steps are repeated until the final 3D model is ready.
Now you would have got an idea that how does a 3D Printer work
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Flexibility in design: An object created using a 3D printing technique can have any type of design, features, even any type of visualization can also be converted into a 3D printed object. Even a designed product can be redesigned according to the need.
- Print when needed: Development of any structures can take place at any time when we need, just the need is of a CAD file and then the printer receives the file and then further operations take place and we get the product.
- Products that are strong and lightweight can be produced for the systems which require them.
- Fast design and Production possible with less management.
- Minimizing Waste, in fact, if we remove some material it can be converted into powders or be melt to use again.
- Cost-effective, as 3D printing saves time with a single step manufacturing, therefore costs associated with different manufacturing machines is reduced hence the overall cost reduces.
Disadvantages of 3D Printing
- Limited Materials can be used.
- Restricted build size, as the size of the model, depends on the size of the build platform and how much it can support.
- Post-processing, additive manufacturing does not require any pre-processing but a lot of post-processing is required, including water jetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, heat drying, cooling, and others, which consumes a lot of time.
- Reduction in jobs
Applications of 3D Printing
- Medical field: Printing of artificial organs for organ transplantation.
- Aerospace Industries: Additive manufacturing has a great impact on aerospace companies as it is used to print or manufacture products with the desired strength and less weight.
- Additive manufacturing technology is now being widely used in the production of metal products and products or objects with complex designs.
- Additive manufacturing is also used to create custom design objects.
- Since now a day metals are also used as material in 3D printing machines, therefore it is widely used in automotive industries.
The scope of additive manufacturing would be rapidly increasing in the coming future. As people are working on this and are trying to make this process much faster by reducing various constraints and modifying the steps in the present process, by this we would be saving many hours, which in turn would increase our manufacturing efficiency.
Future scope of 3D Printing
The 3D Printing process is quite a fascinating process, not much inventory is required and at the same time, the components fabricated using this are robust, of lighter mass, of desired geometry, geometric dimensions, property, and performance, with minimum possible error.
But still, there is a lot of potential of this process that is yet to be discovered, like it can be used in welding, brazing, produce beams for structures, the equipment can be more simple and compact so that it can be repositioned easily as presently they are well supported, mounted with proper fixtures which restrict change in locations. We need to work on the functionality of patterns made as due to heterogeneous nature they react differently when operated vertically or horizontally.
It can also be used in the field of healthcare, like we can create organic products or grow tissue for implants, can make intricate objects, bone for replacement, injection, and other tooling material whenever needed and patients can be cured.
It can lead to a world of customization, where visualization of our customers can be converted into a prototype and then finally in model without help of engineers or professionals with high experience, and we can satisfy our customer or consumer.
These are some of the ideas, there can be more, you would have any other alternate or perfect solution for present problems and also you can have a variety of advanced ideas specialized to additive manufacturing. In Fact, you can work on optimization and better solutions, can eliminate unnecessary repeats, increase the range of size of the product being produced, and many more.
Conclusion
In this blog, I tried to give a thorough idea regarding 3D printing. We know additive manufacturing techniques have enhanced the flexibility of developing products and at the same time made it easier to produce shapes with high complexity, but at the same time, it has some limitations like heterogenous property which arise due to the integration of layers. Now you have an idea of how a 3D printing technology typically works, how a manufacturer employs his idea to print a model in a 3D printer by consuming material of desired property, and what are the various successive steps that occur selectively in a serial order which helps us precisely meet our requirements and build a Model or product.
I hope you all got the idea about 3D printing and how does a 3D printer work. Still, if you have any questions you can comment down, I will try to answer them.