In this blog, you would get to know about CNC machines, CNC programming, and how to do CNC programming. CNC is a very improved means of machining when compared to manually operated machine tools. CNC is fully automated which reduces the chance of error in it. In the present time, there are very much demand for CNC programmers, graduates, and technicians in the various manufacturing department and they are offered a good annual salary. In the CNC machining process, the parts to be manufactured are given the design and its dimension in the CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Then the file is then transferred to post-processing software which converts it into specific codes or commands according to machine requirements and then it is loaded to the CNC machine and we get the desired product. We would be discussing this in detail in this blog.
What is a CNC machine?
CNC machine stands for Computer Numerical Control machine which is a fully automated machine tool. It is controlled by a computer, and instruction is given to a computer in the form of codes (Basically two types of code G-Codes and M-Codes). Therefore it is also referred to as numerically controlled computers. There are three basic parameters in a CNC machine:
- Program with Instruction
- Machine Control Unit
- Processing Equipment
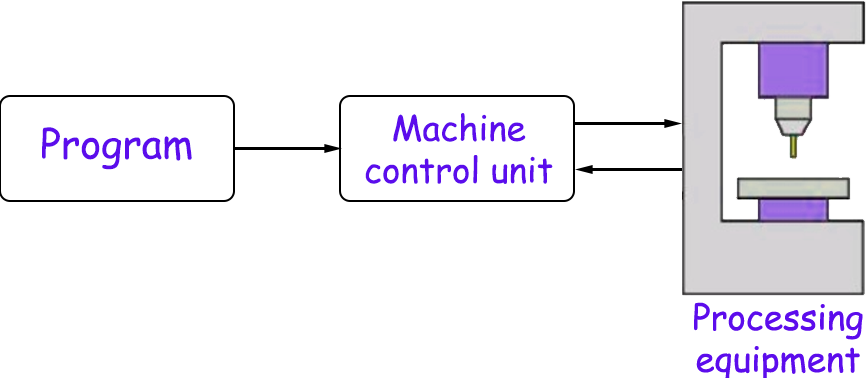
From both manufacturers and the customer point of view, CNC has made it easier and convenient as we can create any type of product, which can be made of metals, aluminum, plastic, wood, or any other material. Machinist or the technician just need to enter a verified program( acts as a memory of machines) which includes every information about the setup, load, path of tool, the radius of holes to be created, the thickness of the workpiece, etc., and then the machine will do the desired machining. Also, it does not require typically skilled operators or a technical team, or a lot of labor to operate it. In today's world, the CNC machining process is used at a huge level in the automotive sector and other mechanical manufacturing sectors. There are various types of CNC Machines. Once a part is designed in CAD software, then CAM software is used to convert or generate codes for the tool motion.
Types of CNC Machines:
- CNC Milling Machine
- CNC Lathe Machine
- CNC Router Machine
- CNC Laser Cutting Machine
- CNC Plasma Cutting Machine
- 5- Axis Machine
- Pick and Place Machine
- 3D Printer
What is CNC Programming?
CNC Programming is used to construct programs to give instructions to the CNC machine tool to work in a particular manner and help us to obtain the desired machined components with specified tolerances and accuracy. With the help of programming manufacturing processes become more efficient and flexible, we can perform any complex operations, produce a wide range of finished products, and many more.
Some software used for programming in CNC are:
CNC program consists of a combination of machine tool code and machine-specific instructions. It contains
- Information about the geometry
- Motion detail to move the cutting tool
- Cutting speed details
- Feed details
- Miscellaneous functions such as coolant on and off, spindle direction, etc.
We can define the complete CNC machining process by the following blocks:
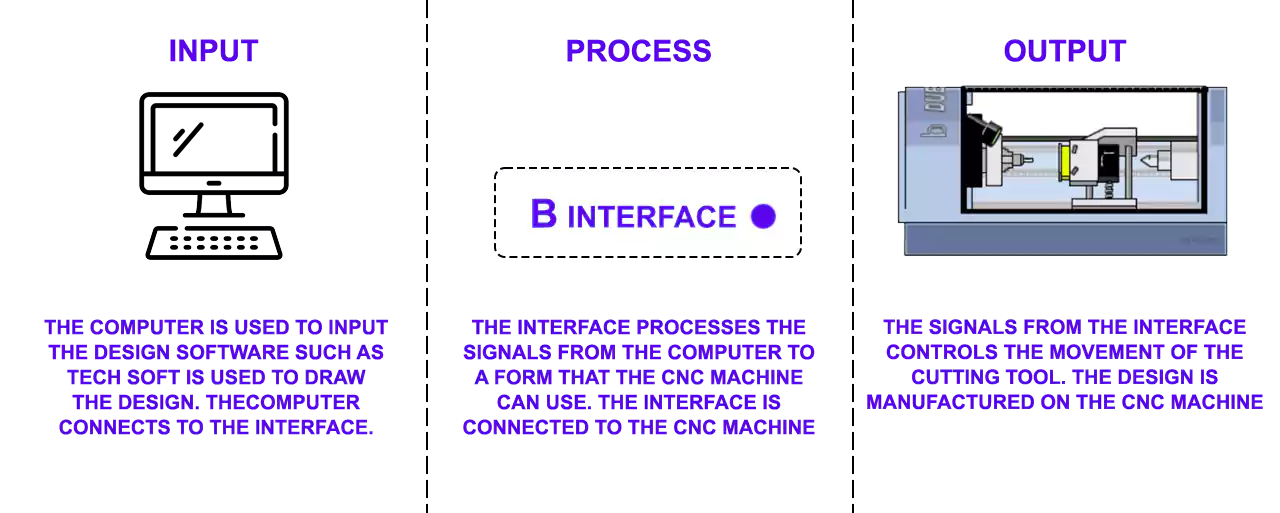
How to do CNC Programming:
CNC programming is all about the entry of data in form of codes. We need to define the positions and movement of the tool in order to ensure and guarantee proper machining of the metal workpiece. A CNC machine has two axes where it works, namely X-axis and Y-axis. In a CNC Lathe, the X-axis controls the diameter of the component whereas Z-axis controls the length of the component. To start a CNC program it is important to call the right cutting tool for machining first. Eg. T7 or T0707
Now talking about the structure of the program, the program is written in the following structure:
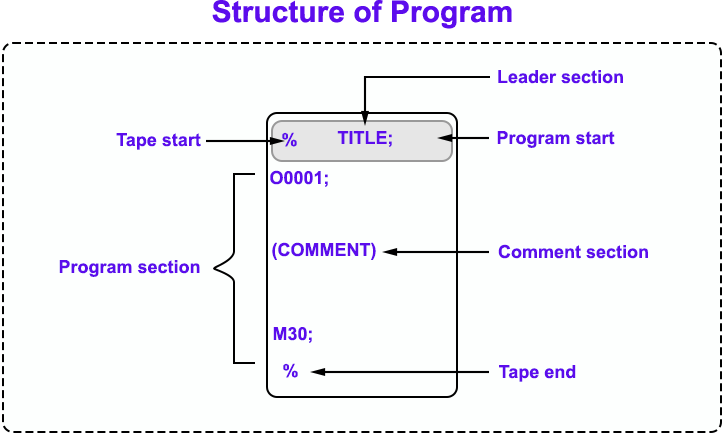
The basic modes of programming language in CNC machines are namely G-Codes and M-Codes. As a CNC programmer, you need to what is G and M codes. Now let's understand the basic difference between the two.
G-Codes: They are also referred to as preparatory codes. This code tells the machine tool what type of action is to be performed. Any word in a CNC program that starts with the letter G is a G-Code. Each G- code is defined with fixed documentation to enable them to reach the destination. G-Codes gives instructions to machine tools in which way it should go, with how much feed, at what feed rates, how much height and depth is to be cut, how much offsets, etc.
For eg. To travel straight G01, in a curve G02, etc. Following are the list of G-Codes and their functions:
G Codes Their Function
G00 Positioning at rapid travel;
G01 Linear interpolation using a feed rate;
G02 Circular interpolation clockwise;
G03 Circular interpolation, counterclockwise;
G04 Dwell
G10 Set working datum position;
G17 Select X-Y plane;
G18 Select Z-X plane;
G19 Select Z-Y plane;
G20 Imperial units;
G21 Metric units;
G27 Reference return check;
G28 Automatic return through reference point;
G29 used to move to a location through a reference point;
G31 Skip function;
G32 Thread cutting operation on a Lathe;
G33 Thread cutting operation on a Mill;
G40 Cancel cutter compensation;
G41 Cutter compensation left;
G42 Cutter compensation right;
G43 Tool length compensation;
G44 Tool length compensation;
G50 Set coordinate system (Mill), maximum RPM (Lathe);
G52 Local coordinate system setting;
G53 Machine coordinate system setting;
G54 and G59 Set Datum;
G70 Finish cycle (Lathe);
G71 Rough turning cycle (Lathe);
G72 Rough facing cycle (Lathe);
G73 Chip break drilling cycle;
G74 Left hand tapping Mill;
G74 Face grooving cycle;
G75 OD groove pecking cycle (Lathe);
G76 Boring cycle;
G76 Screw cutting cycle (Lathe);
G80 Cancel cycles;
G81 Drill cycle;
G82 Drill cycle with dwell;
G83 Peck drilling cycle;
G84 Tapping cycle;
G85 Bore in, bore out;
G86 Bore in, rapid out;
G87 Back boring cycle;
G90 Absolute programming;
G91 Incremental programming;
G92 Reposition origin point;
G92 Screw thread cutting cycle (Lathe);
G94 Per minute feed;
G95 Per revolution feed;
G96 Constant surface speed (Lathe);
G97 Constant surface speed cancel;
G98 Feed per minute (Lathe);
G99 Feed per revolution (Lathe)
M-Codes: These codes are related to the working of CNC machines and their hardware. It tells the machine-like when to start and when to stop, spinning directions, etc. Any word in a CNC program that starts with the letter M is an M-Code. Following is the list of M-Codes and their function.
Code Their Functions
M00 Compulsory stop
M01 Optional stop
M02 End of program
M03 The spindle on (clockwise rotation)
M04 The spindle on (counterclockwise rotation)
M05 Spindle stop
M06 Automatic tool change (ATC)
M07 Coolant on (mist)
M08 Coolant on (flood)
M09 Coolant off
M10 Pallet clamp-on
M11 Pallet clamp off
M13 The spindle on (clockwise rotation) and coolant on (flood)
M19 Spindle orientation
M21 Mirror, X-axis
M21 Tailstock forward
M22 Mirror, Y-axis
M22 Tailstock backward
M23 Mirror OFF
M23 Thread gradual pullout ON
M24 Thread gradual pullout OFF
M30 End of program, with a return to program top
M41 Gear select – gear 1
M42 Gear select – gear 2
M43 Gear select – gear 3
M44 Gear select – gear 4
M48 Feedrate override allowed
M49 Feedrate override NOT allowed
M52 Unload the Lastest tool from the spindle
M60 Automatic pallet change (APC)
M98 Subprogram call
M99 Subprogram end
M100 Clean Nozzle
Now we precisely know about coordinates and how to establish a program. At the same time, we can probe out complete knowledge from a given CNC program. A CNC program is written in multiple lines each of then is referred to as a block. Some blocks are common in most of the processes, each block defines which tool to be used and corresponds to the controller about what is to be done on the workpieces. Following is a standard format of the CNC program:

Now let start with CNC programming and understand the very basic CNC program. Let's write a program to set the controls of the CNC machine for prototyping and producing the following model of given dimensions with help of a simple turning operation.
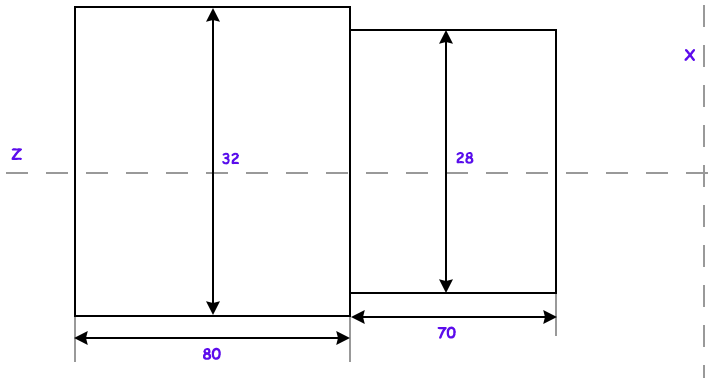
N1 G90 G71 G94 F100; # Program run in an absolute coordinate system, metric input, feed in mm/min, feed 100
N2 G28 X0 Z0; # Reference point/home position tool at X0 and Z0
N3 M06 T06 D01; # Tool Change command, select tool no 6, tool offset 01
N4 M03 S1000; # Spindle clockwise at speed 1000
N5 M07; # Coolant on
N6 G00 X32 Z2; # Tool travel rapidly at X32 and Z2
N7 G01 X31 Z0; # Tool moves linearly at X31 and Z0
N8 G01 X31 Z-70; # Tool start cutting linearly X31 and Z-70
N9 G00 X32 Z-70; # Tool away at X-axis from cutting position and Z-axis at the same place
N10 G00 X32 Z2; # Tool at the same place at X-axis and Z-axis away from job linearly
N11 G01 X30 Z0; # It takes another position at X-30 and Z0 ready for the second cut
N12 G01 X30 Z-70; # It takes second cut X30 and Z -70
N13 G00 X32 Z-70; # Tool away at X-axis from cutting position and Z-axis at the same place
N14 G00 X32 Z2; # Tool at the same place at X-axis and Z-axis away from job linearly
N15 G01 X29 Z0; # It takes another position at X-29 and Z0 ready for the second cut
N16 G01 X29 Z-70; # It takes third cut X29 and Z -70
N17 G00 X32 Z-70; # Tool away at X-axis from cutting position and Z-axis at the same place
N18 G00 X32 Z2; # Tool at the same place at X-axis and Z-axis away from job linearly
N19 G01 X28 Z0; # It takes another position at X-28 and Z0 ready for the second cut
N20 G01 X28 Z-70; # It takes fourth cut X28 and Z -70
N21 G00 X32 Z2; # I goes to a safe position from working position rapidly
N22 G28 X0 Z0; # Tool goes to reference point/home position
N23 M05; # Spindle off
N24 M09; # Cooling off
N25 M30; # End of the main program
We just started with the development of basic drawing using CNC systems, but industrial drawings have a more complex profile. We will learn and address various model which industry or organization requires and are commonly used in the field of engineering and we will be establishing their program in our future blogs.
Conclusion:
CNC is a quite useful technology in the field of production industries. Any type of workpiece with the required geometric shape, tolerance can be produced easily with the help of this advanced machinery with high precision. A variety of processes can be done with help of these technologies. Fabrication of shapes of any material, any custom piece, with the precise and complex features can be done easily with help of different types of CNC tooling. Nowadays CNC technology is employed on lathes, mills, grinding machines, and on another traditional operator which makes them computerized, and the movements and other capabilities of these machines depend on how the machine is programmed, now all processes can be done without the help of any specialized machinists with high skills. Also from service or occupational point of view, there very much demand of workforce, thus high opportunities of employment and you have a great career in this field with high wages.
In this blog, we got an idea about the fundamentals and basics of CNC programming, and how to do CNC programming. This is just an introduction part there are much more things to define. We would be discussing advanced programing in the next blog. Hope the basics of CNC programming are clear to you now. Still, if you have any questions you can comment down, I will try to answer them.