Hello Cyber Learners,
In this blog, we will explore the fascinating world of digital forensics and the techniques and tools used to collect, analyze, and interpret data from electronic devices. Whether you are a law enforcement professional, legal practitioner, or simply someone interested in the field of digital forensics, this blog will provide you with an introduction to the basics of digital forensic investigations.
Throughout this blog, we will also discuss the legal and ethical considerations surrounding digital forensic investigations, as well as the challenges and limitations of working with digital evidence. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid understanding of the field of digital forensics and the techniques and tools used to conduct successful investigations.
So let's get started...
- What is Digital Forensics?
- What is Computer Forensics?
- Who is Digital Forensics Investigator?
- Objectives of Digital Forensics
- What are the Advantages of Digital Forensics?
- What are the Disadvantages of Digital Forensics?
- Phases Of Digital Forensics
- Career Options In Digital Forensics
- Digital Forensics Jobs
What is Digital Forensics?
Digital forensics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and preserving electronic data in order to investigate and prevent cybercrime, fraud, or other types of digital misconduct. It involves the use of specialized tools and techniques to recover and examine data from various digital devices and storage media, such as computers, smartphones, and servers.
What is Computer Forensics?
Computer forensics, also known as digital forensics or cyber forensics, is a branch of digital forensics that involves the investigation and analysis of digital data to gather evidence for use in legal or investigative proceedings. It is the process of identifying, preserving, analyzing, and presenting digital evidence in a manner that is admissible in a court of law.
The aim of computer forensics is to provide accurate, reliable and admissible evidence that can be used in legal proceedings or other types of investigations.
Que 1: Is Ditial Forensics And Computer Forensics both are same?
Ans: Digital forensics and computer forensics are related but not exactly the same thing. Digital forensics is a broader field that encompasses computer forensics as well as other types of digital devices. Computer forensics, on the other hand, specifically deals with the investigation of computer-related crimes, and involves the collection, analysis, and preservation of data from computers, computer networks, and other digital devices for use in investigations and legal proceedings. Therefore, while the two terms are related, they are not interchangeable.
Who is Digital Forensics Investigator?
A digital forensic investigator is a professional who specializes in the analysis and investigation of electronic devices and digital information. They are responsible for examining digital devices, such as computers, smartphones, and servers, to recover, analyze and preserve electronic data for use in legal proceedings or investigations.
Objectives of Digital Forensics
The primary objective of digital forensics is to identify, collect, preserve, and analyze electronic data in a way that is legally admissible and scientifically sound. More specifically, digital forensics aims to:
- Investigate cybercrime: Digital forensics is used to investigate cybercrimes such as hacking, identity theft, and other forms of online fraud. For Example, If a cyber criminal installs malware in an organisation system then by analysing the malware activities we can catch the cyber criminal by finding the IP address, and which port is used for communication.
- Recover lost or deleted data: Digital forensics can be used to recover lost or deleted data from electronic devices, including files that have been intentionally or accidentally deleted. For Example, If cyber criminals delete the files and software before catching then with the help of memory forensics we can recover the files and software which he/she used for criminal activities.
- Support legal proceedings: Digital forensics is used to gather and analyze electronic evidence that can be presented in a court of law or other legal proceedings. For Example In order to punish cyber-criminals investigators need to collect all evidence from the system.
- Prevent digital misconduct: Digital forensics can help prevent digital misconduct by identifying security vulnerabilities and providing insights into the methods and techniques used by cybercriminals.
- Protect critical infrastructure: Digital forensics is used to protect critical infrastructure, such as power grids, communication networks, and financial systems, by identifying and mitigating potential cyber threats.
What are the Advantages of Digital Forensics?
There are several advantages to using digital forensics in investigations and legal proceedings:
- Digital evidence can be gathered and analyzed quickly and efficiently.
- Digital forensics can often recover evidence that may have been destroyed or hidden in traditional investigations.
- The use of digital forensics can help to establish a more accurate timeline of events, which can be critical in determining the sequence of events leading up to a crime.
- Digital evidence can be analyzed remotely, which can reduce the need for travel and save time and money.
What are the Disadvantages of Digital Forensics?
While digital forensics has many advantages, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider.
- Digital evidence can be easily altered or deleted, which can make it difficult to determine its authenticity.
- The sheer volume of digital data that can be collected can be overwhelming and time-consuming to analyze.
- Digital forensic tools can be expensive and may require specialized training to use effectively.
- Digital evidence can be easily manipulated by experienced hackers or cybercriminals, who may attempt to cover their tracks or plant false evidence.
Phases Of Digital Forensics
Digital forensics is a complex and multi-step process that is designed to collect and analyze digital evidence in a way that is both legally admissible and scientifically sound. The following is a more detailed description of the steps involved in digital forensics:
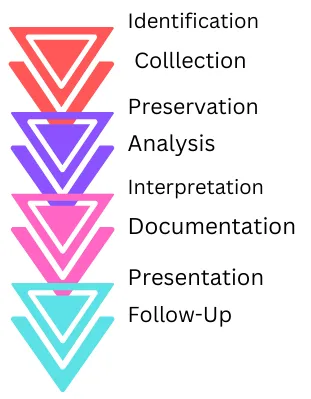
- Identification: The first step in digital forensics is to identify the digital devices or systems that are relevant to the case. This might include computers, smartphones, servers, or other electronic devices that could contain evidence related to the case.
- Collection: Once the relevant devices have been identified, digital evidence is collected. This involves using appropriate methods to ensure that the evidence is not altered or destroyed during the collection process. Collection methods may include the use of specialized software, hardware, or manual techniques such as taking photographs or making copies of the data.
- Preservation: Once the digital evidence has been collected, it must be properly preserved. This involves ensuring that the evidence is not tampered with or modified in any way and that it is stored securely in order to prevent loss or damage. Proper documentation and chain of custody procedures are also critical at this stage.
- Analysis: The analysis stage involves using specialized software and techniques to examine and analyze the digital evidence. This may include searching for specific keywords or patterns, recovering deleted files or data, or reading metadata to identify important information such as file creation dates or user account information.
- Interpretation: Once the digital evidence has been analyzed, the next step is to make sense of the information that has been collected. This may involve identifying patterns or relationships that could help establish facts in the case or using the evidence to confirm or refute a hypothesis.
- Documentation: It is important to document the entire process in order to ensure that the findings are admissible in court. This includes creating detailed reports that document the methods used, the findings, and the chain of custody of the digital evidence.
- Presentation: The findings must be presented in a clear and understandable way that is relevant to the case, such as in a court of law or to other stakeholders. This may involve the use of visual aids, such as graphs or charts, to help explain complex information in a way that is easy to understand.
- Follow-up: Digital forensics is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to continue monitoring and managing the digital evidence throughout the case. This may involve further analysis or investigation if new evidence is uncovered, or if additional information is required to help establish the facts in the case.
Career Options In Digital Forensics
With the rise of computer hacking, government organizations, financial institutions and reputable companies are recruiting qualified digital forensics to secure digital assets and identify and prevent cyber threats. There is no shortage of digital forensics job
Digital Forensics Jobs
A candidate who possesses the required skills and educational qualifications can pursue any of the following positions:
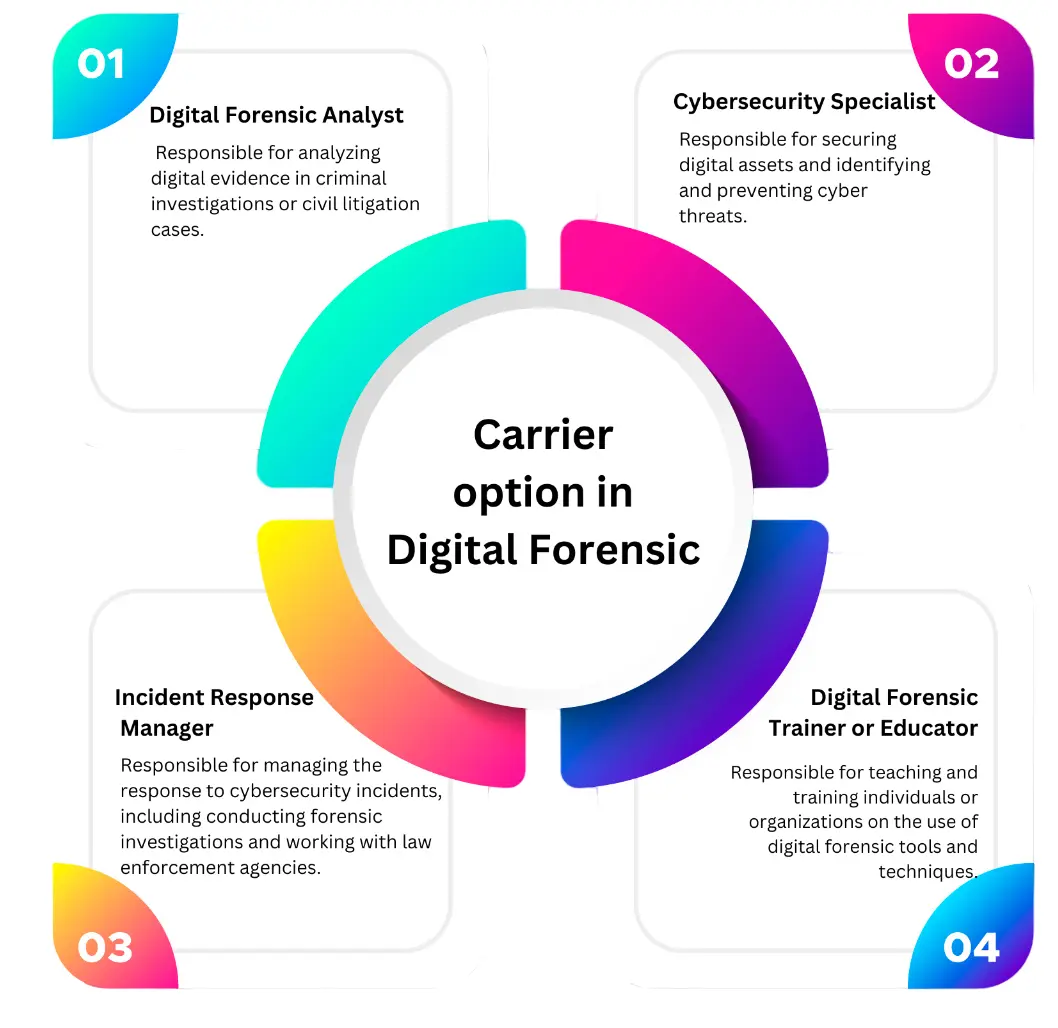
1. Digital Forensic Analyst
A Digital Forensic Analyst is responsible for conducting thorough analyses of electronic data as part of investigations and legal proceedings.They use specialized tools and techniques to identify, collect, preserve, and analyze digital evidence.They may be involved in a variety of cases, including cybercrime, fraud, and intellectual property theft.
2. Cybersecurity Specialist
A Cybersecurity Specialist is responsible for protecting digital assets from unauthorized access, theft, and damage.They must have a strong understanding of computer networks, operating systems, and security protocols.They develop and implement security policies and procedures, conduct risk assessments, and monitor systems for potential vulnerabilities or threats.
3. Incident Response Manager
An Incident Response Manager is responsible for managing the response to cybersecurity incidents, including conducting forensic investigations and coordinating with internal teams and external stakeholders. They must have a deep understanding of cybersecurity threats and be able to respond quickly and effectively to mitigate any potential damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital forensics plays a critical role in modern-day investigations, particularly as technology continues to advance and people become increasingly reliant on digital devices. The use of digital forensic techniques and tools allows investigators to collect, preserve, and analyze electronic data to support legal proceedings and bring criminals to justice.
However, as technology continues to evolve, digital forensic practitioners must remain up-to-date with the latest developments and techniques in order to ensure that they are able to effectively carry out their work. Overall, digital forensics is a complex and rapidly evolving field that is essential in the fight against cybercrime and other types of digital offences.
Que 4: How Digital Forensic Investigator is different from Traditional Forensics?
Ans: Digital forensics involves the collection, preservation, and analysis of electronic data to support investigations and legal proceedings. Traditional forensics typically involves the collection and analysis of physical evidence from crime scenes. Digital forensics requires specialized tools and techniques to identify and recover digital evidence, which can be volatile and easily destroyed.
Also Read
- What is OSINT? | OSINT Framework | Tools for OSINT | Best OSINT Techniques
- What is Packet Sniffing | How to Perform Packet Sniffing | Practical Demo On Wireshark
- What is Smurf Attack? | What is the Denial of Service Attack? | Practical DDoS Attack Step-By-Step Guide
- What is DoS Attack | How to do Denial of Service Attack [Practical Demo]
- What is Packet Sniffing? | How to Perform Packet Sniffing | Practical Demo on Wireshark
- What is Metasploit Framework | What is Penetration Testing | How to use Metasploit
- How to Install Metasploit on Windows and Linux | [Step by Step Guide]
- How to Use Metasploit | Metasploit Commands | Metasploit Tutorial